Ectopic expression of Cripto-1 in transgenic mouse embryos causes hemorrhages, fatal cardiac defects and embryonic lethality
- PMID: 27687577
- PMCID: PMC5043281
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34501
Ectopic expression of Cripto-1 in transgenic mouse embryos causes hemorrhages, fatal cardiac defects and embryonic lethality
Abstract
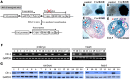
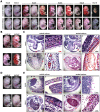
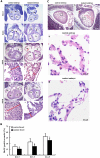
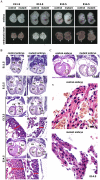
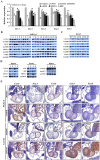
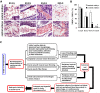
Targeted disruption of Cripto-1 in mice caused embryonic lethality at E7.5, whereas we unexpectedly found that ectopic Cripto-1 expression in mouse embryos also led to embryonic lethality, which prompted us to characterize the causes and mechanisms underlying embryonic death due to ectopic Cripto-1 expression. RCLG/EIIa-Cre embryos displayed complex phenotypes between embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) and E17.5, including fatal hemorrhages (E14.5-E15.5), embryo resorption (E14.5-E17.5), pale body surface (E14.5-E16.5) and no abnormal appearance (E14.5-E16.5). Macroscopic and histological examination revealed that ectopic expression of Cripto-1 transgene in RCLG/EIIa-Cre embryos resulted in lethal cardiac defects, as evidenced by cardiac malformations, myocardial thinning, failed assembly of striated myofibrils and lack of heartbeat. In addition, Cripto-1 transgene activation beginning after E8.5 also caused the aforementioned lethal cardiac defects in mouse embryos. Furthermore, ectopic Cripto-1 expression in embryonic hearts reduced the expression of cardiac transcription factors, which is at least partially responsible for the aforementioned lethal cardiac defects. Our results suggest that hemorrhages and cardiac abnormalities are two important lethal factors in Cripto-1 transgenic mice. Taken together, these findings are the first to demonstrate that sustained Cripto-1 transgene expression after E11.5 causes fatal hemorrhages and lethal cardiac defects, leading to embryonic death at E14.5-17.5.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiac abnormalities cause early lethality of jumonji mutant mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Nov 26;324(4):1319-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.203. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15504358
-
Alcohol consumption during gestation causes histone3 lysine9 hyperacetylation and an alternation of expression of heart development-related genes in mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Sep;38(9):2396-402. doi: 10.1111/acer.12518. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25257289
-
Partial rescue of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1) knock-out mouse by transgenic expression of NCX1.Exp Mol Med. 2003 Apr 30;35(2):125-35. doi: 10.1038/emm.2003.18. Exp Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12754417
-
Ubiquitous expression of Akt1 p.(E17K) results in vascular defects and embryonic lethality in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Dec 18;29(20):3350-3360. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa216. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 33030203 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto-1: an embryonic gene that promotes tumorigenesis.Future Oncol. 2010 Jul;6(7):1127-42. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.68. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20624125 Review.
Cited by
-
A Multidisciplinary Review of the Roles of Cripto in the Scientific Literature Through a Bibliometric Analysis of its Biological Roles.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;12(6):1480. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061480. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo and in vitro study of co-expression of LMP1 and Cripto-1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Sep-Oct;86(5):617-625. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 May 20. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31375471 Free PMC article.
-
Cripto Is Targeted by miR-1a-3p in a Mouse Model of Heart Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;24(15):12251. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512251. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569627 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-specific over-expression of Cripto-1 in transgenic mice promotes hepatocyte proliferation and deregulated expression of hepatocarcinogenesis-related genes and signaling pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 13;13(17):21155-21190. doi: 10.18632/aging.203402. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34517344 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive and conditional gene knockout mice for the study of intervertebral disc degeneration: Current status, decision considerations, and future possibilities.JOR Spine. 2023 Jan 7;6(1):e1242. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1242. eCollection 2023 Mar. JOR Spine. 2023. PMID: 36994464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gidekel S., Pizov G., Bergman Y. & Pikarsky E. Oct-3/4 is a dose-dependent oncogenic fate determinant. Cancer Cell 4, 361–370 (2003). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

