Comparison of saddle, lumbar epidural and caudal blocks on anal sphincter tone: A prospective, randomized study
- PMID: 27688685
- PMCID: PMC5536558
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060516659393
Comparison of saddle, lumbar epidural and caudal blocks on anal sphincter tone: A prospective, randomized study
Abstract
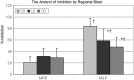
Objective To compare the effects of saddle, lumbar epidural and caudal blocks on anal sphincter tone using anorectal manometry. Methods Patients undergoing elective anorectal surgery with regional anaesthesia were divided randomly into three groups and received a saddle (SD), lumbar epidural (LE), or caudal (CD) block. Anorectal manometry was performed before and 30 min after each regional block. The degree of motor blockade of the anal sphincter was compared using the maximal resting pressure (MRP) and the maximal squeezing pressure (MSP). Results The study analysis population consisted of 49 patients (SD group, n = 18; LE group, n = 16; CD group, n = 15). No significant differences were observed in the percentage inhibition of the MRP among the three regional anaesthetic groups. However, percentage inhibition of the MSP was significantly greater in the SD group (83.6 ± 13.7%) compared with the LE group (58.4 ± 19.8%) and the CD group (47.8 ± 16.9%). In all groups, MSP was reduced significantly more than MRP after each regional block. Conclusions Saddle block was more effective than lumbar epidural or caudal block for depressing anal sphincter tone. No differences were detected between lumbar epidural and caudal blocks.
Keywords: Anorectal surgery; anal sphincter tone; anorectal manometry; caudal block; lumbar epidural block; saddle block.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Changes in anal canal pressure during caudal and lumbar epidural anesthesia].Masui. 1994 Oct;43(10):1524-8. Masui. 1994. PMID: 7815704 Japanese.
-
Anorectal manometry assessment of sphincter relaxation after local-regional anesthesia with posterior perineal block.Ann Ital Chir. 2019;90:580-582. Ann Ital Chir. 2019. PMID: 31929173
-
Local anesthetic infiltration versus caudal epidural block for anorectal surgery: a randomized controlled trial.J Clin Anesth. 2007 Jun;19(4):269-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2006.12.004. J Clin Anesth. 2007. PMID: 17572321 Clinical Trial.
-
Anesthesia for ambulatory anorectal surgery.Medicina (Kaunas). 2004;40(2):101-11. Medicina (Kaunas). 2004. PMID: 15007268 Review. English, Lithuanian.
-
Fecal incontinence. Studies on physiology, pathophysiology and surgical treatment.Dan Med Bull. 2003 Aug;50(3):262-82. Dan Med Bull. 2003. PMID: 13677243 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of Caudal Epidural Injection on healing in the treatment of chronic anal fissure.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 15;102(37):e35160. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035160. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37713828 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Caudal Epidural Blocks and Spinal Anesthesia for Anorectal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Pain Ther. 2022 Jun;11(2):713-721. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00389-7. Epub 2022 May 2. Pain Ther. 2022. PMID: 35501468 Free PMC article.
-
Major complications of caudal block: A prospective survey of 973 cases in adult anorectal surgery.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 6;9(10):e20759. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20759. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37860549 Free PMC article.
-
A Response to: Letter to the Editor Regarding "Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Caudal Epidural Blocks and Spinal Anesthesia for Anorectal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial".Pain Ther. 2022 Dec;11(4):1503-1505. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00420-x. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Pain Ther. 2022. PMID: 35974227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
General versus general anaesthesia combined with caudal block in laparoscopic-assisted Soave pull-through of Hirschsprung disease: a retrospective study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2021 Aug 30;21(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01431-5. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 34461833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li S, Coloma M, White PF, et al. Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery. Anesthesiology 2000; 93: 1225–1230. - PubMed
-
- Erdman AG. Concise anatomy for anaesthesia, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2001.
-
- Davies SJ, Paech MJ, Welch H, et al. Maternal experience during epidural or combined spinal-epidural anesthesia for cesarean section: a prospective, randomized trial. Anesth Analg 1997; 85: 607–613. - PubMed
-
- Karaman S, Akercan F, Akarsu T, et al. Comparison of the maternal and neonatal effects of epidural block and of combined spinal-epidural block for Caesarean section. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2005; 121: 18–23. - PubMed
-
- Verghese ST, Mostello LA, Patel RI, et al. Testing anal sphincter tone predicts the effectiveness of caudal analgesia in children. Anesth Analg 2002; 94: 1161–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

