Interferon-α reduces the gefitinib sensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 27688730
- PMCID: PMC5032161
- DOI: 10.5114/wo.2016.61853
Interferon-α reduces the gefitinib sensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Aim of the study: Many studies have shown that interferon-α (IFN-α) enhances the antiproliferative effect of gefitinib in some solid tumours. We aimed to determine the effect of combining IFN-α with gefitinib in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines (A549, H1299, HCC827) with different EGFR and K-Ras gene statuses.
Material and methods: An MTT assay was used to assess cell proliferation. Apoptosis was detected by an Annexin V/propidium iodide assay using flow cytometry, and western blotting was used to determine the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor/phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/p-EGFR) and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3/phosphorylated signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3/p-STAT3).
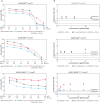
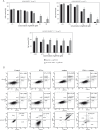
Results: There was an additive interaction when gefitinib was combined with IFN-α in all cell lines; however, there was antagonism when gefitinib followed IFN-α pretreatment in three cell lines. Notably, IFN-α pretreatment significantly reduced the gefitinib sensitivity of HCC827 cells. Surprisingly, while IFN-α inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation in cell lines, gefitinib could do so.
Conclusions: The results might confirm the hypothesis that IFN-α induces gefitinib sensitivity of NSCLC, and IFN-α inhibits phosphorylation of STAT3, which may be dependent on EGFR signal activation playing a role in the reduction of gefitinib sensitivity after IFN-α treatment in NSCLC cell lines.
Keywords: STAT3; antagonism; gefitinib; interferon-α; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Baselga J, Averbuch SD. ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) as an anticancer agent. Drugs. 2000;60(Suppl 1):33–40. discussion 41-32. - PubMed
-
- Amato RJ, Jac J, Hernandez-McClain J. Interferon-alpha in combination with either imatinib (Gleevec) or gefitinib (Iressa) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a phase II trial. Anticancer Drugs. 2008;19:527–33. - PubMed
-
- Huether A, Hopfner M, Sutter AP, Schuppan D, Scherübl H. Erlotinib induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatocellular cancer cells and enhances chemosensitivity towards cytostatics. J Hepatol. 2005;43:661–9. - PubMed
-
- Yang JL, Qu XJ, Hayes VM, Brenner PC, Russell PJ, Goldstein D. Erlotinib (OSI-774)-induced inhibition of transitional cell carcinoma of bladder cell line growth is enhanced by interferon-alpha. BJU Int. 2007;99:1539–45. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Wang F, He F, Huang L. The effect of combining interferon-alpha and gefitinib in human colon cancer cell lines. West Indian Med J. 2011;60:107–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
