Proficiency testing of skin prick testers as part of a quality assurance system
- PMID: 27688875
- PMCID: PMC5034588
- DOI: 10.1186/s13601-016-0126-7
Proficiency testing of skin prick testers as part of a quality assurance system
Abstract
Background: Skin prick test is an important diagnostic procedure in clinical allergy but documentation of the quality is often missing.
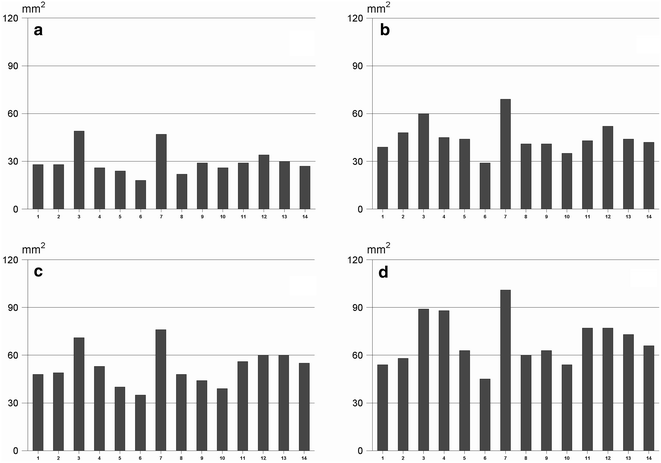
Methods: We describe a proficiency system to evaluate staff members in relation to the international recommended reproducibility in terms of coefficient of variation (CV < 40 %) and the linearity (coefficient of regression >0.85) based on blinded octuplicate histamine testing using histamine 3, 10, 30 and 100 mg/ml.
Results: Fourteen trained allergy nurses participated in the proficiency testing. More than 95 % of the nurses, generated coefficient of variation less than 40 %, and for around 35 % of testers the CV were below 20 % based on wheal area. Regarding the linearity (coefficient of regression), only two nurses produced tests with a value below 0.85. On the contrary, 79 % of testers demonstrated a coefficient of regression >0.95. Depending on the gentleness of the prick procedure, the inter-nurse variability in wheal area varied more than twofold corresponding to a 10-doubling of histamine concentration. This would never have been detected without using a proficiency testing system.
Conclusion: The described histamine testing provides an objective system for the evaluation of basic skin test quality assessment standards especially for documentation in scientific studies.
Keywords: Coefficient of regression; Coefficient of variation; Histamine skin prick test; Quality assessment; Reproducibility.
Figures


References
-
- Bernstein IL, Li JT, Bernstein DI, et al. Allergy diagnostic testing: an update practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;100(Suppl):3. - PubMed
-
- Dreborg S. Skin tests used in type I allergy testing. EAACI position paper. Allergy. 1989;10(44):59. - PubMed
-
- Dreborg S, Frew A. Allergen standardization and skin tests. EAACI position paper. Allergy. 1993;14(48):49–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

