Acute kidney injury in patients with paraquat intoxication; a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 27689124
- PMCID: PMC5039990
- DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2016.43
Acute kidney injury in patients with paraquat intoxication; a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
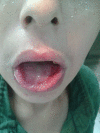
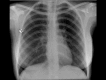
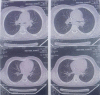
Paraquat and diquat are classified as bipyridyl compounds not only leads to acute organ damage, but also to a variety of complications. Patients with severe paraquat-induced poisoning may succumb to multiple organ failure involving the circulatory and respiratory systems. Deliberate self-poisoning with paraquat continues to be a major public health concern in many developing countries. At present there is no specific antidote to paraquat poisoning, hence the need to more focus on prevention and in cases of poisoning aggressive decontamination to prevent further absorption. This article presented a 12-year-old male with acute kidney injury following the ingestion of paraquat in suicidal attempt and serves to explore the complications associated with paraquat poisoning and current recommended treatment.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Paraquat; Poisoning; Suicide.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources