Protective effect of Schizandrin B against damage of UVB irradiated skin cells depend on inhibition of inflammatory pathways
- PMID: 27689692
- PMCID: PMC5172505
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2016.1227572
Protective effect of Schizandrin B against damage of UVB irradiated skin cells depend on inhibition of inflammatory pathways
Abstract
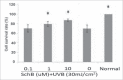
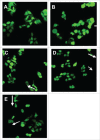
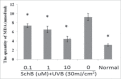
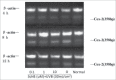
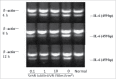
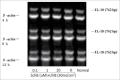
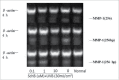
Schizandrin B is extracted from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. This study evaluated the photoprotective effect of Schizandrin B on oxidative stress injury of the skin caused by UVB-irradiation and the molecular mechanism of the photoprotective effect of Schizandrin B, and we firstly found that Schizandrin B could block Cox-2, IL-6 and IL-18 signal pathway to protect damage of skin cells given by UVB-irradiation. In the research, we found that Schizandrin B can attenuate the UVB-induced toxicity on keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts in human body, and can outstandingly eliminated intracellular ROS produced by UVB-irradiation. These results demonstrate that Schizandrin B can regulate the function of decreasing intracellular SOD's activity and increasing the expression level of MDA in HaCaT cells result from the guidance of UVB, and it markedly reduced the production of inflammatory factors such as Cox-2, IL-6 or IL-18, decreased the expression level of MMP-1, and interdicted degradation process of collagens in UVB-radiated cells. Therefore, skin keratinocytes can be effectively protected from UVB-radiated damage by Schizandrin B, and UVB-irradiation caused inflammatory responses can be inhibited by attenuating process of ROS generating.
Keywords: COX-2; ROS; Schizandrin B; UVB-irradiation; collagen; photoaging.
Figures


References
-
- Kappes UP, Luo D, Potter M, Schulmeister K, Rünger TM. Runger.Short- and long-wave UV light (UVB and UVA) induce similar mutations in human skin cells. J Invest Dermatol 2006; 126(3):667-75; PMID:16374481; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700093 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ji C, Yang B, Yang Z, Tu Y, Yang YL, He L, Bi ZG. Ultra-violet B (UVB)-induced skin cell death occurs through a cyclophilin D intrinsic signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 425(4):825-9; PMID:22892127; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.160 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Laethem A, Claerhout S, Garmyn M, Agostinis P. The sunburn cell:regulation of death and survival of the keratinocyte. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005; 37(8):1547-53; PMID:15896663; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2005.02.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ito T, Seo N, Yagita H, Tsujimura K, Takigawa M, Tokura Y. Alterations of immune functions in barrier disrupted skin by UVB irradiation. J Dermatol Sci 2003; 33(3):151-9; PMID:14643520; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0923-1811(03)00177-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fischer TW, Zbytek B, Sayre RM, Apostolov EO, Basnakian AG, Sweatman TW, Wortsman J, Elsner P, Slominski A. Melatonin increases survival of HaCaT keratinocytes by suppressing UV-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res 2006; 40(1):18-26; PMID:16313494; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00273.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
