Temporal proteomic analysis of HIV infection reveals remodelling of the host phosphoproteome by lentiviral Vif variants
- PMID: 27690223
- PMCID: PMC5085607
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.18296
Temporal proteomic analysis of HIV infection reveals remodelling of the host phosphoproteome by lentiviral Vif variants
Abstract
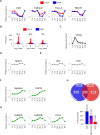
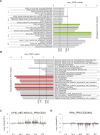
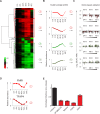
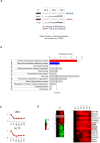
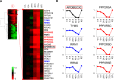
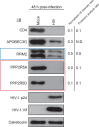
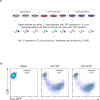
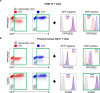
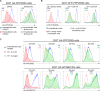
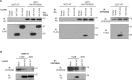
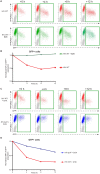
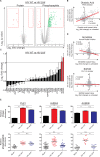
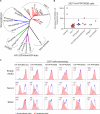
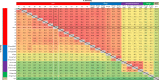
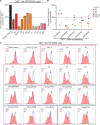
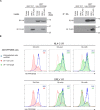
Viruses manipulate host factors to enhance their replication and evade cellular restriction. We used multiplex tandem mass tag (TMT)-based whole cell proteomics to perform a comprehensive time course analysis of >6500 viral and cellular proteins during HIV infection. To enable specific functional predictions, we categorized cellular proteins regulated by HIV according to their patterns of temporal expression. We focussed on proteins depleted with similar kinetics to APOBEC3C, and found the viral accessory protein Vif to be necessary and sufficient for CUL5-dependent proteasomal degradation of all members of the B56 family of regulatory subunits of the key cellular phosphatase PP2A (PPP2R5A-E). Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of HIV-infected cells confirmed Vif-dependent hyperphosphorylation of >200 cellular proteins, particularly substrates of the aurora kinases. The ability of Vif to target PPP2R5 subunits is found in primate and non-primate lentiviral lineages, and remodeling of the cellular phosphoproteome is therefore a second ancient and conserved Vif function.
Keywords: HIV; PP2A; Vif; human; infectious disease; lentivirus; microbiology; phosphorylation; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional and Structural Insights into a Vif/PPP2R5 Complex Elucidated Using Patient HIV-1 Isolates and Computational Modeling.J Virol. 2020 Oct 14;94(21):e00631-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00631-20. Print 2020 Oct 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32847850 Free PMC article.
-
ARIH2 Is a Vif-Dependent Regulator of CUL5-Mediated APOBEC3G Degradation in HIV Infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2019 Jul 10;26(1):86-99.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Cell Host Microbe. 2019. PMID: 31253590 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Conservation of PP2A Antagonism and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in Maedi-Visna Virus Vif.Viruses. 2022 Aug 1;14(8):1701. doi: 10.3390/v14081701. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016323 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Vif, APOBEC, and intrinsic immunity.Retrovirology. 2008 Jun 24;5:51. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-51. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18577210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CBFß and HIV Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;962:415-431. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28299671 Review.
Cited by
-
Virus-host protein co-expression networks reveal temporal organization and strategies of viral infection.iScience. 2023 Nov 16;26(12):108475. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108475. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38077135 Free PMC article.
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Vpr Mediates Degradation of APC1, a Scaffolding Component of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome.J Virol. 2021 Jul 12;95(15):e0097120. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00971-20. Epub 2021 Jul 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34011540 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory metabolic networks in pancreatic cancers upon perturbation of glutamine metabolism.Nat Commun. 2017 Jul 3;8:15965. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15965. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28671190 Free PMC article.
-
SCASP: A Simple and Robust SDS-Aided Sample Preparation Method for Proteomic Research.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021;20:100051. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2021.100051. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33549647 Free PMC article.
-
Altered memory CCR6+ Th17-polarised T-cell function and biology in people with HIV under successful antiretroviral therapy and HIV elite controllers.EBioMedicine. 2024 Sep;107:105274. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105274. Epub 2024 Aug 22. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39178742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldauf HM, Pan X, Erikson E, Schmidt S, Daddacha W, Burggraf M, Schenkova K, Ambiel I, Wabnitz G, Gramberg T, Panitz S, Flory E, Landau NR, Sertel S, Rutsch F, Lasitschka F, Kim B, König R, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. SAMHD1 restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4(+) T cells. Nature Medicine. 2012;18:1682–1687. doi: 10.1038/nm.2964. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

