Glucuronidation and UGT isozymes in bladder: new targets for the treatment of uroepithelial carcinomas?
- PMID: 27690298
- PMCID: PMC5356909
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12277
Glucuronidation and UGT isozymes in bladder: new targets for the treatment of uroepithelial carcinomas?
Abstract
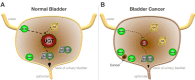
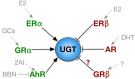
Bladder cancer has been linked to numerous toxins which can be concentrated in the bladder after being absorbed into the blood and filtered by the kidneys. Excessive carcinogenic load to the bladder urothelium may result in the development of cancer. However, enzymes within the bladder can metabolize carcinogens into substrates that are safer. Importantly, these proteins, namely the UGT's (uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases), have been shown to possibly prevent bladder cancer. Also, studies have shown that the UGT1 expression is decreased in uroepithelial carcinomas, which may allow for the accumulation of carcinogens in the bladder. In this review, we discuss the UGT system and its' protective role against bladder cancer, UGT genetic mutations that modulate risk from chemicals and environmental toxins, as well as targeting of the UGT enzymes by nuclear receptors.
Keywords: UDP-G glycosyltransferase; UGT; bladder cancer; glucuronidation; nuclear receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society - Key Statistics for Bladder cancer. 2016.
-
- Jankovic S, Radosavljevic V. Risk factors for bladder cancer. Tumori. 2007;93(1):4–12. - PubMed
-
- Vineis P, Simonato L. Proportion of lung and bladder cancers in males resulting from occupation: a systematic approach. Archives of environmental health. 1991;46(1):6–15. - PubMed
-
- Goebell PJ, Villanueva CM, Rettenmeier AW, Rubben H, Kogevinas M. Environmental exposure, chlorinated drinking water, and bladder cancer. World journal of urology. 2004;21(6):424–432. - PubMed
-
- Komulainen H, Kosma VM, Vaittinen SL, Vartiainen T, Kaliste-Korhonen E, Lotjonen S, Tuominen RK, Tuomisto J. Carcinogenicity of the drinking water mutagen 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5H)-furanone in the rat. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1997;89(12):848–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

