Viral RNA switch mediates the dynamic control of flavivirus replicase recruitment by genome cyclization
- PMID: 27692070
- PMCID: PMC5101012
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.17636
Viral RNA switch mediates the dynamic control of flavivirus replicase recruitment by genome cyclization
Abstract
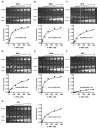
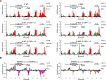
Viral replicase recruitment and long-range RNA interactions are essential for RNA virus replication, yet the mechanism of their interplay remains elusive. Flaviviruses include numerous important human pathogens, e.g., dengue virus (DENV) and Zika virus (ZIKV). Here, we revealed a highly conserved, conformation-tunable cis-acting element named 5'-UAR-flanking stem (UFS) in the flavivirus genomic 5' terminus. We demonstrated that the UFS was critical for efficient NS5 recruitment and viral RNA synthesis in different flaviviruses. Interestingly, stabilization of the DENV UFS impaired both genome cyclization and vRNA replication. Moreover, the UFS unwound in response to genome cyclization, leading to the decreased affinity of NS5 for the viral 5' end. Thus, we propose that the UFS is switched by genome cyclization to regulate dynamic RdRp binding for vRNA replication. This study demonstrates that the UFS enables communication between flavivirus genome cyclization and RdRp recruitment, highlighting the presence of switch-like mechanisms among RNA viruses.
Keywords: biochemistry; cis-acting element; flavivirus; genome cyclization; infectious disease; microbiology; viral RNA structure; viral replicase recruitment; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

















References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

