Urinary Tract Infection: Pathogenesis and Outlook
- PMID: 27692880
- PMCID: PMC5159206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.09.003
Urinary Tract Infection: Pathogenesis and Outlook
Abstract
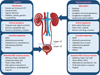
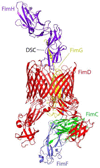
The clinical syndromes comprising urinary tract infection (UTI) continue to exert significant impact on millions of patients worldwide, most of whom are otherwise healthy women. Antibiotic therapy for acute cystitis does not prevent recurrences, which plague up to one fourth of women after an initial UTI. Rising antimicrobial resistance among uropathogenic bacteria further complicates therapeutic decisions, necessitating new approaches based on fundamental biological investigation. In this review, we highlight contemporary advances in the field of UTI pathogenesis and how these might inform both our clinical perspective and future scientific priorities.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; cystitis; pyelonephritis; urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
D.A.H. serves on the Board of Directors of BioVersys AG, Basel, Switzerland.
Figures
References
-
- Harding GK, Ronald AR. The management of urinary infections: what have we learned in the past decade? Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1994;4:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Foxman B. Urinary tract infection syndromes: occurrence, recurrence, bacteriology, risk factors, and disease burden. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2014;28:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Gupta K, et al. Increasing antimicrobial resistance and the management of uncomplicated community-acquired urinary tract infections. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

