Genetics of human lupus nephritis
- PMID: 27693588
- PMCID: PMC5373939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.09.012
Genetics of human lupus nephritis
Abstract
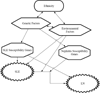
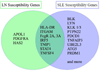
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by immune complex formation with multi-organ manifestations. Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most severe types of organ damage in SLE, and it clearly contributes to increased morbidity and mortality due to SLE. LN occurs more frequently and is more severe in non-European ancestral backgrounds, although the cause of this disparity remains largely unknown. Genetic factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE. Although many SLE susceptibility genes have been identified, the genetic basis of LN is not as well understood. While some of the established general SLE susceptibility genes are associated with LN, recent discoveries highlight a number of genes with renal functions that are specifically associated with LN. Some of these genes associated with LN help to explain the disparity in the prevalence of nephritis between individuals with SLE, and also partially explain differences in LN between ancestral backgrounds. Moreover, not only the gene mutations, but also post-translational modifications seem to play important roles in the pathogenesis of LN. Overall it seems likely that a combination of general SLE susceptibility genes cooperate with LN specific risk genes to result in the genetic propensity for LN. In this review, we will outline the genetic contribution to LN and describe possible roles of LN susceptibility genes.
Keywords: APOL1; Genetics; HAS2; Lupus nephritis; PDGFR; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England journal of medicine. 2011;365:2110–2121. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez E, Rasmussen A, Riba L, Acevedo-Vasquez E, Kelly JA, Langefeld CD, Williams AH, Ziegler JT, Comeau ME, Marion MC, Garcia-De La Torre I, Maradiaga-Cecena MA, Cardiel MH, Esquivel-Valerio JA, Rodriguez-Amado J, Moctezuma JF, Miranda P, Perandones CE, Castel C, Laborde HA, Alba P, Musuruana JL, Goecke IA, Anaya JM, Kaufman KM, Adler A, Glenn SB, Brown EE, Alarcon GS, Kimberly RP, Edberg JC, Vila LM, Criswell LA, Gilkeson GS, Niewold TB, Martin J, Vyse TJ, Boackle SA, Ramsey-Goldman R, Scofield RH, Petri M, Merrill JT, Reveille JD, Tsao BP, Orozco L, Baca V, Moser KL, Gaffney PM, James JA, Harley JB, Tusie-Luna T, Pons-Estel BA, Jacob CO, Alarcon-Riquelme ME. Impact of genetic ancestry and sociodemographic status on the clinical expression of systemic lupus erythematosus in American Indian-European populations. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2012;64:3687–3694. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borchers AT, Leibushor N, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. Lupus nephritis: a critical review. Autoimmunity reviews. 2012;12:174–194. - PubMed
-
- Borchers AT, Naguwa SM, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME. The geoepidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity reviews. 2010;9:A277–A287. - PubMed
-
- Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L, Horwitz D, Bachman B, Roy-Burman P, Walker A, Mack TM. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1992;35:311–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

