Nucleobases Undergo Dynamic Rearrangements during RNA Tertiary Folding
- PMID: 27693721
- PMCID: PMC5085838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.09.015
Nucleobases Undergo Dynamic Rearrangements during RNA Tertiary Folding
Abstract
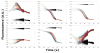
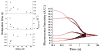
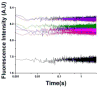
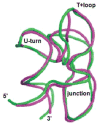
The tertiary structure of the GTPase center (GAC) of 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) as seen in cocrystals is extremely compact. It is stabilized by long-range hydrogen bonds and nucleobase stacking and by a triloop that forms within its three-way junction. Its folding pathway from secondary structure to tertiary structure has not been previously observed, but it was shown to require Mg2+ ions in equilibrium experiments. The fluorescent nucleotide 2-aminopurine was substituted at selected sites within the 60-nt GAC. Fluorescence intensity changes upon addition of MgCl2 were monitored over a time-course from 1ms to 100s as the RNA folds. The folding pathway is revealed here to be hierarchical through several intermediates. Observation of the nucleobases during folding provides a new perspective on the process and the pathway, revealing the dynamics of nucleobase conformational exchange during the folding transitions.
Keywords: 2-aminopurine fluorescence; GTPase center RNA; RNA folding kinetics; stopped-flow fluorescence.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
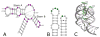

References
-
- Conn GL, Gittis AG, Lattman EE, Misra VK, Draper DE. A compact RNA tertiary structure contains a buried backbone-K+ complex. J Mol Biol. 2002;318:963–73. - PubMed
-
- Wimberly BT, Guymon R, McCutcheon JP, White SW, Ramakrishnan V. A detailed view of a ribosomal active site: the structure of the L11-RNA complex. Cell. 1999;97:491–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

