Managing eosinophilic esophagitis: challenges and solutions
- PMID: 27695356
- PMCID: PMC5033215
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S78428
Managing eosinophilic esophagitis: challenges and solutions
Abstract
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic and progressive immune-mediated condition defined by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and dense eosinophilic infiltration of the esophageal mucosa. Therapies consist of anti-eosinophilic medications and specialized diets aimed to decrease the progression of EoE and alleviate its symptoms, namely, dysphagia and food impaction. Assessing response to therapy remains challenging, as treatment end points are not well defined and currently consist of clinical, histologic, and endoscopic features. Newer validated measures may help standardize treatment end points. Emerging data support the use of maintenance therapy, which may reduce disease progression. Optimal dosages, delivery techniques, and duration of treatment need to be determined. When features of fibrostenosis develop, esophageal dilation is a safe and effective adjunctive strategy for improving symptoms. In EoE cases refractory to conventional treatments, newer therapies targeting inflammatory mediators and cytokines are on the horizon.
Keywords: allergy; corticosteroids; dietary treatment; dilation; dysphagia; eosinophilia; eosinophilic esophagitis; esophagitis.
Figures
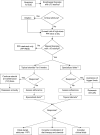
References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, et al. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–692. quiz 693. - PubMed
-
- Lipka S, Keshishian J, Boyce HW, Estores D, Richter JE. The natural history of steroid-naive eosinophilic esophagitis in adults treated with endoscopic dilation and proton pump inhibitor therapy over a mean duration of nearly 14 years. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;80:592–598. - PubMed
-
- Keshishian J, Vrcel V, Boyce HW, Estores D, Serrano J, Richter JE. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a paradigm shift for pathology. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48:607–612. - PubMed
-
- Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1230–1236.e1-2. - PubMed
-
- Kuchen T, Straumann A, Safroneeva E, et al. Swallowed topical corticosteroids reduce the risk for long-lasting bolus impactions in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy. 2014;69:1248–1254. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

