Therapeutic and routine prophylactic properties of rFactor VIII Fc (efraloctocog alfa, Eloctate®) in hemophilia A
- PMID: 27695377
- PMCID: PMC5028163
- DOI: 10.2147/JBM.S80814
Therapeutic and routine prophylactic properties of rFactor VIII Fc (efraloctocog alfa, Eloctate®) in hemophilia A
Abstract
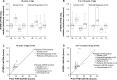
rFVIIIFc (efraloctocog alfa, Eloctate®) is an extended half-life (EHL) factor VIII licensed for use in patients with hemophilia A for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding and surgical episodes. Pharmacokinetic studies in adults have shown a mean 1.5-fold increase in half-life compared to full-length factor VIII. When compared to adults, the half-life is decreased by 8% in adolescents between 12 and 17 years, by 18% in children 6 to <12 years, and by 33% in children between the ages of 2 and <6 years. There is a considerable interindividual variation in the prolongation of the half-life particularly in children and across the age groups, the range extending from no increase to a 2.5-fold increase. In addition to age, von willebrand factor (VWF) antigen level has demonstrated a significant impact on rFVIIIFc half-life, with higher VWF levels associated with greater prolongation of half-life. The pivotal and pediatric clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of rFVIIIFc for use in regular prophylaxis and in management of bleeds and surgery. In these studies, just under half the participants showed a zero annualized bleed rate (ABR), and the median ABR (1.6 in the pivotal study for the individualized prophylaxis arm) showed a further decrease in the extension study. On average, the patients required fewer infusions (reduced by at least a third), and the mean weekly consumption seems to be in keeping with standard recombinant factor VIII. EHL rFVIIIFc has made decreased infusion frequency a possibility. However, the interindividual variability in dose and infusion frequency highlights the need for a personalized approach based on individual patient's half-life and/or response to treatment.
Keywords: FVIII; efraloctocog alfa; extended half-life factors; hemophilia A; prophylaxis; rFVIIIFc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-utility analysis of life-long prophylaxis with recombinant factor VIIIFc vs recombinant factor VIII for the management of severe hemophilia A in Sweden.J Med Econ. 2018 Apr;21(4):318-325. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2017.1405816. Epub 2017 Dec 4. J Med Econ. 2018. PMID: 29139314 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of two extended half-life FVIII concentrates (Eloctate and Adynovate) in adolescents with hemophilia A: Is there a difference?J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Jul;17(7):1085-1096. doi: 10.1111/jth.14469. Epub 2019 Jun 2. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31038793
-
Recombinant FVIIIFc Versus BAY 94-9027 for Treatment of Patients with Haemophilia A: Comparative Efficacy Using a Matching Adjusted Indirect Comparison.Adv Ther. 2021 Feb;38(2):1263-1274. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01599-1. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33377987 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Efficacy and Consumption of rVIII-SingleChain Versus Two Recombinant FVIII Products Used for Prophylactic Treatment of Adults/Adolescents with Severe Haemophilia A.Adv Ther. 2021 Sep;38(9):4872-4884. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01853-0. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34368918 Free PMC article.
-
Status of Recombinant Factor VIII Concentrate Treatment for Hemophilia a in Italy: Characteristics and Clinical Benefits.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Dec 3;6:261. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00261. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31850352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness of recombinant factor VIII Fc versus emicizumab for prophylaxis in adults and adolescents with haemophilia A without inhibitors in the UK.Eur J Haematol. 2023 Mar;110(3):262-270. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13901. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Eur J Haematol. 2023. PMID: 36398467 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed doses of N8-GP prophylaxis maintain moderate-to-mild factor VIII levels in the majority of patients with severe hemophilia A.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019 Jun 11;3(3):542-554. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12220. eCollection 2019 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31294338 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Quality of Life, Adherence, and Kinesiophobia in Patients with Hemophilia Treated with Extended Half-Life Treatment: Final Results of the LongHest Project.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;17(7):835. doi: 10.3390/ph17070835. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065686 Free PMC article.
-
Limited sampling strategies for accurate determination of extended half-life factor VIII pharmacokinetics in severe haemophilia A patients.Haemophilia. 2021 May;27(3):408-416. doi: 10.1111/hae.14288. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Haemophilia. 2021. PMID: 33742733 Free PMC article.
-
Direct comparison of two extended-half-life recombinant FVIII products: a randomized, crossover pharmacokinetic study in patients with severe hemophilia A.Ann Hematol. 2019 Sep;98(9):2035-2044. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03747-2. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Ann Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31236667 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Stonebraker JS, Bolton-Maggs PH, Soucie JM, Walker I, Brooker M. A study of variations in the reported haemophilia A prevalence around the world. Haemophilia. 2010;16(1):20–32. - PubMed
-
- Mannucci PM, Tuddenham EG. The hemophilias – from royal genes to gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(23):1773–1779. - PubMed
-
- White GC, 2nd, Rosendaal F, Aledort LM, Lusher JM, Rothschild C, Ingerslev J. Definitions in hemophilia. Recommendation of the scientific subcommittee on factor VIII and factor IX of the scientific and standardization committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 2001;85(3):560. - PubMed
-
- Lee CA. Textbook of Hemophilia. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd; 2014. Front matter; pp. i–xxi.
-
- Reitter S, Waldhoer T, Vutuc C, Lechner K, Pabinger I. Survival in a cohort of patients with haemophilia at the haemophilia care center in Vienna, Austria, from 1983 to 2006. Haemophilia. 2009;15(4):888–893. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

