The Paracoccus denitrificans NarK-like nitrate and nitrite transporters-probing nitrate uptake and nitrate/nitrite exchange mechanisms
- PMID: 27696579
- PMCID: PMC5217062
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13546
The Paracoccus denitrificans NarK-like nitrate and nitrite transporters-probing nitrate uptake and nitrate/nitrite exchange mechanisms
Abstract
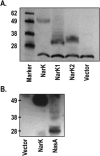
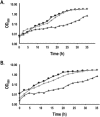
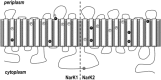
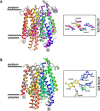
Nitrate and nitrite transport across biological membranes is often facilitated by protein transporters that are members of the major facilitator superfamily. Paracoccus denitrificans contains an unusual arrangement whereby two of these transporters, NarK1 and NarK2, are fused into a single protein, NarK, which delivers nitrate to the respiratory nitrate reductase and transfers the product, nitrite, to the periplasm. Our complementation studies, using a mutant lacking the nitrate/proton symporter NasA from the assimilatory nitrate reductase pathway, support that NarK1 functions as a nitrate/proton symporter while NarK2 is a nitrate/nitrite antiporter. Through the same experimental system, we find that Escherichia coli NarK and NarU can complement deletions in both narK and nasA in P. denitrificans, suggesting that, while these proteins are most likely nitrate/nitrite antiporters, they can also act in the net uptake of nitrate. Finally, we argue that primary sequence analysis and structural modelling do not readily explain why NasA, NarK1 and NarK2, as well as other transporters from this protein family, have such different functions, ranging from net nitrate uptake to nitrate/nitrite exchange.
© 2016 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Abramson, J. , Smirnova, I. , Kasho, V. , Verner, G. , Kaback, H.R. , and Iwata, S. (2003) Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli . Science 301: 610–615. - PubMed
-
- Abramson, J. , Iwata, S. , and Kaback, H.R. (2004) Lactose permease as a paradigm for membrane transport proteins. Mol Membr Biol 21: 227–236. - PubMed
-
- Alefounder, P.R. , Mccarthy, J.E.G. , and Ferguson, S.J. (1981) The basis of the control of nitrate reduction by oxygen in Paracoccus dentrificans . FEMS Microbiol Lett 12: 321–326.
-
- Boogerd, F.C. , Vanverseveld, H.W. , and Stouthamer, A.H. (1983) Dissimilatory nitrate uptake in Paracoccus denitrificans via a ‐dependent system and a nitrate‐nitrite antiport system. Biochim Biophys Acta 723: 415–427.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

