Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Compared to Blind Steroid Injections in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- PMID: 27696773
- PMCID: PMC5376367
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.23108
Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Compared to Blind Steroid Injections in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of ultrasound-guided injections to blind injections in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) in a large community-based cohort.
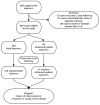
Methods: This study evaluated residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, treated with a corticosteroid injection for CTS between 2001 and 2010. The proportion of patients receiving retreatment and the duration of retreatment-free survival between blind and ultrasound-guided injections were compared. Propensity score matching was used to control for confounding by indication.
Results: In the matched data set consisting of 234 (of 600) hands treated with a blind injection and 87 (of 89) ultrasound-guided injection cases, ultrasound guidance was associated with a reduced hazard of retreatment (hazard ratio 0.59 [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.37-0.93]). In addition, ultrasound guidance was associated with 55% reduced odds of retreatment within 1 year compared to blind injections (adjusted odds ratio 0.45 [95% CI 0.24-0.83]).
Conclusion: This study indicates that ultrasound-guided injections are more effective in comparison to blind injections in the treatment of CTS.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Comment in
-
Comparison of the Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Steroid Injections and Blind Steroid Injections in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Comment on the Article by Evers et al.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Nov;70(11):1717-1718. doi: 10.1002/acr.23450. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 29045073 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marshall S, Tardif G, Ashworth N. Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. The Cochrane database of systematc reviews. 2007;(2):CD001554. - PubMed
-
- Huisstede BM, Hoogvliet P, Randsdorp MS, Glerum S, van Middelkoop M, Koes BW. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Part I: effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments--a systematic review. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2010;91(7):981–1004. - PubMed
-
- Green DP. Diagnostic and therapeutic value of carpal tunnel injection. The Journal of hand surgery. 1984;9(6):850–4. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JK, Sevier TL. A review of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome. Disability and rehabilitation. 2003;25(3):113–9. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, Jang JE, Park BK. Anatomical basis of ulnar approach in carpal tunnel injection. Pain physician. 2013;16(3):E191–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials