Sphingolipids in mitochondria
- PMID: 27697478
- PMCID: PMC5125891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.019
Sphingolipids in mitochondria
Abstract
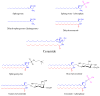
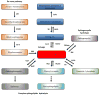
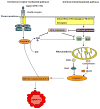
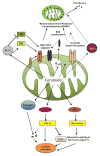
Sphingolipids are bioactive lipids found in cell membranes that exert a critical role in signal transduction. In recent years, it has become apparent that sphingolipids participate in growth, senescence, differentiation and apoptosis. The anabolism and catabolism of sphingolipids occur in discrete subcellular locations and consist of a strictly regulated and interconnected network, with ceramide as the central hub. Altered sphingolipid metabolism is linked to several human diseases. Hence, an advanced knowledge of how and where sphingolipids are metabolized is of paramount importance in order to understand the role of sphingolipids in cellular functions. In this review, we provide an overview of sphingolipid metabolism. We focus on the distinct pathways of ceramide synthesis, highlighting the mitochondrial ceramide generation, transport of ceramide to mitochondria and its role in the regulation of mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, mitophagy and implications to disease. We will discuss unanswered questions and exciting future directions. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Lipids of Mitochondria edited by Guenther Daum.
Keywords: Cancer; Ceramide; Mitochondrial apoptosis; Mitophagy; Sphingolipid metabolism.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Goni FM, Alonso A. Biophysics of sphingolipids I. Membrane properties of sphingosine, ceramides and other simple sphingolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1902–1921. - PubMed
-
- Simons K, Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:139–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

