The OncoArray Consortium: A Network for Understanding the Genetic Architecture of Common Cancers
- PMID: 27697780
- PMCID: PMC5224974
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0106
The OncoArray Consortium: A Network for Understanding the Genetic Architecture of Common Cancers
Abstract
Background: Common cancers develop through a multistep process often including inherited susceptibility. Collaboration among multiple institutions, and funding from multiple sources, has allowed the development of an inexpensive genotyping microarray, the OncoArray. The array includes a genome-wide backbone, comprising 230,000 SNPs tagging most common genetic variants, together with dense mapping of known susceptibility regions, rare variants from sequencing experiments, pharmacogenetic markers, and cancer-related traits.
Methods: The OncoArray can be genotyped using a novel technology developed by Illumina to facilitate efficient genotyping. The consortium developed standard approaches for selecting SNPs for study, for quality control of markers, and for ancestry analysis. The array was genotyped at selected sites and with prespecified replicate samples to permit evaluation of genotyping accuracy among centers and by ethnic background.
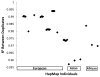
Results: The OncoArray consortium genotyped 447,705 samples. A total of 494,763 SNPs passed quality control steps with a sample success rate of 97% of the samples. Participating sites performed ancestry analysis using a common set of markers and a scoring algorithm based on principal components analysis.
Conclusions: Results from these analyses will enable researchers to identify new susceptibility loci, perform fine-mapping of new or known loci associated with either single or multiple cancers, assess the degree of overlap in cancer causation and pleiotropic effects of loci that have been identified for disease-specific risk, and jointly model genetic, environmental, and lifestyle-related exposures.
Impact: Ongoing analyses will shed light on etiology and risk assessment for many types of cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev; 26(1); 126-35. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- International WCRF. Lung Cancer Statistics. 2012 [cited 2015 May 2]; Available from: http://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/data-specific-cancers/lung-....
-
- Chakravarti A. Population genetics--making sense out of sequence. NatGenet. 1999;21:56–60. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Schork NJ. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994;265:2037–48. - PubMed
-
- Reich DE, Lander ES. On the allelic spectrum of human disease. Trends Genet. 2001;17:502–10. - PubMed
-
- Houlston RS, Peto J. The search for low-penetrance cancer susceptibility alleles. Oncogene. 2004;23:6471–6. - PubMed
Online Resources Used
-
- Hindorff LA, MacArthur J, European Bioinformatics Institute, Morales J, European Bioinformatics Institute, Junkins HA, Hall PN, Klemm AK, Manolio TA. A Catalog of Published Genome-Wide Association Studies. [cited 2016 May 2]. Available at: https://www.genome.gov/26525384/catalog-of-published-genomewide-associat...
-
- Burdett T, EBI, Hall PN, NHGRI, Hastings E, EBI, Hindorff LA, NHGRI, Junkins HA, NHGRI, Klemm AK, NHGRI, MacArthur J, EBI, Manolio TA, NHGRI, Morales J, EBI, Parkinson H, EBI, Welter D., EBI The NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies. Available at: www.ebi.ac.uk/gwasAccessed [cited 2016 May 2], version [v1.0]
-
- FastPop [software] 2015 May 8; [cited 2016 May 2]. Available from: http://sourceforge.net/projects/fastpop/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 17528/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 20861/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA138313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 LM012204/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA134286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103534/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190182/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA196386/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA192393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- P50 CA136393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 23382/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

