Multiscale implementation of infinite-swap replica exchange molecular dynamics
- PMID: 27698148
- PMCID: PMC5081654
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1605089113
Multiscale implementation of infinite-swap replica exchange molecular dynamics
Abstract
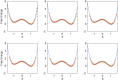
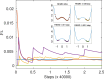
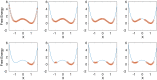
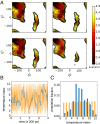
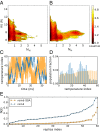
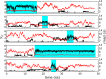
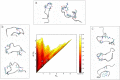
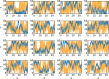
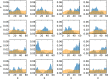
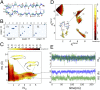
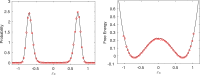
Replica exchange molecular dynamics (REMD) is a popular method to accelerate conformational sampling of complex molecular systems. The idea is to run several replicas of the system in parallel at different temperatures that are swapped periodically. These swaps are typically attempted every few MD steps and accepted or rejected according to a Metropolis-Hastings criterion. This guarantees that the joint distribution of the composite system of replicas is the normalized sum of the symmetrized product of the canonical distributions of these replicas at the different temperatures. Here we propose a different implementation of REMD in which (i) the swaps obey a continuous-time Markov jump process implemented via Gillespie's stochastic simulation algorithm (SSA), which also samples exactly the aforementioned joint distribution and has the advantage of being rejection free, and (ii) this REMD-SSA is combined with the heterogeneous multiscale method to accelerate the rate of the swaps and reach the so-called infinite-swap limit that is known to optimize sampling efficiency. The method is easy to implement and can be trivially parallelized. Here we illustrate its accuracy and efficiency on the examples of alanine dipeptide in vacuum and C-terminal β-hairpin of protein G in explicit solvent. In this latter example, our results indicate that the landscape of the protein is a triple funnel with two folded structures and one misfolded structure that are stabilized by H-bonds.
Keywords: HMM; REMD; SSA; importance sampling; protein-folding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Replica exchange molecular dynamics method for protein folding simulation.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;350:205-23. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-189-4:205. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 16957325
-
TIGER2: an improved algorithm for temperature intervals with global exchange of replicas.J Chem Phys. 2009 May 7;130(17):174106. doi: 10.1063/1.3129342. J Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19425768 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the replica-exchange molecular-dynamics method for efficient sampling in the temperature space.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2015 May;91(5):052708. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.91.052708. Epub 2015 May 18. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2015. PMID: 26066200
-
Influence of various parameters in the replica-exchange molecular dynamics method: Number of replicas, replica-exchange frequency, and thermostat coupling time constant.Biophys Physicobiol. 2018 Aug 8;15:165-172. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.15.0_165. eCollection 2018. Biophys Physicobiol. 2018. PMID: 30250775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of biological membranes and membrane proteins using enhanced conformational sampling algorithms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jul;1858(7 Pt B):1635-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.12.032. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26766517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Structural Dynamics As Captured by Molecular Simulations: A Comprehensive Overview.Chem Rev. 2018 Apr 25;118(8):4177-4338. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00427. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29297679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stratified UWHAM and Its Stochastic Approximation for Multicanonical Simulations Which Are Far from Equilibrium.J Chem Theory Comput. 2017 Oct 10;13(10):4660-4674. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.7b00651. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Chem Theory Comput. 2017. PMID: 28902500 Free PMC article.
-
Exchanging Replicas with Unequal Cost, Infinitely and Permanently.J Phys Chem A. 2022 Dec 1;126(47):8878-8886. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.2c06004. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Phys Chem A. 2022. PMID: 36394633 Free PMC article.
-
Order and interactions in DNA arrays: Multiscale molecular dynamics simulation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 6;7(1):4775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05109-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28684875 Free PMC article.
-
MoDAFold: a strategy for predicting the structure of missense mutant protein based on AlphaFold2 and molecular dynamics.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):bbae006. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae006. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38305456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giberti F, Salvalaglio M, Mazzotti M, Parrinello M. Insight into the nucleation of urea crystals from the melt. Chem Eng Sci. 2015;121:51–59.
-
- Dror RO, et al. Structural basis for modulation of a G-protein-coupled receptor by allosteric drugs. Nature. 2013;503(7475):295–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

