Raf kinase inhibitor protein regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cells apoptosis through the NF-κB and ERK pathways
- PMID: 27698534
- PMCID: PMC5018566
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.15-128
Raf kinase inhibitor protein regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cells apoptosis through the NF-κB and ERK pathways
Abstract
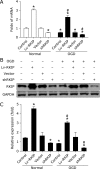
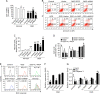
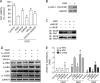
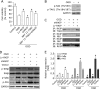
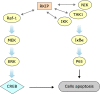
Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) is a critical molecule for cellular responses to stimuli. In this study, we investigated whether RKIP is responsible for neural cell apoptosis induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and explored the role of NF-κB and ERK pathways regulated by RKIP under OGD stimuli. RKIP was overexpressed or knocked down using lentivirus in PC12 cells, which were then challenged by OGD. RKIP overexpression significantly increased the cell viability of OGD cells, and attenuated apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reactive oxygen species generation. RKIP knockdown induced reverse effects. Moreover, we found that RKIP interacted with TAK1, NIK, IKK, and Raf-1 and negatively regulated the NF-κB and ERK pathways. RKIP overexpression significantly inhibited IKK, IκBα, and P65 phosphorylation in NF-κB pathway and MEK, ERK, and CREB phosphorylation in ERK pathway, respectively. RKIP knockdown induced reverse effects. Furthermore, a NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 and a MEK inhibitor U0126 blocked the changes caused by RKIP down-regulation after OGD. In conclusion, these results demonstrate that RKIP plays a key role in neural cell apoptosis caused by OGD partly via regulating NF-κB and ERK pathways. The present study may provide new insights into the role of RKIP in ischemic stroke.
Keywords: ERK pathway; NF-κB pathway; OGD; PC12 cells; RKIP.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al.; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131:e29–e322. - PubMed
-
- Martin R, Lloyd H, Cowan A. The early events of oxygen and glucose deprivation: setting the scene for neuronal death? Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:251–257. - PubMed
-
- Sawe N, Steinberg G, Zhao H. Dual roles of the MAPK/ERK1/2 cell signaling pathway after stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86:1659–1669. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Chen S, Jiang Y, et al. Minocycline reduces oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cell cytotoxicity via matrix metalloproteinase-9, integrin β1 and phosphorylated Akt modulation. Neurol Sci. 2013;34:1391–1396. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

