Dexamethasone and Monophosphoryl Lipid A-Modulated Dendritic Cells Promote Antigen-Specific Tolerogenic Properties on Naive and Memory CD4+ T Cells
- PMID: 27698654
- PMCID: PMC5027201
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00359
Dexamethasone and Monophosphoryl Lipid A-Modulated Dendritic Cells Promote Antigen-Specific Tolerogenic Properties on Naive and Memory CD4+ T Cells
Abstract
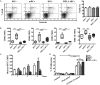
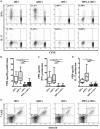
Tolerogenic dendritic cells (DCs) are a promising tool to control T cell-mediated autoimmunity. Here, we evaluate the ability of dexamethasone-modulated and monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA)-activated DCs [MPLA-tolerogenic DCs (tDCs)] to exert immunomodulatory effects on naive and memory CD4+ T cells in an antigen-specific manner. For this purpose, MPLA-tDCs were loaded with purified protein derivative (PPD) as antigen and co-cultured with autologous naive or memory CD4+ T cells. Lymphocytes were re-challenged with autologous PPD-pulsed mature DCs (mDCs), evaluating proliferation and cytokine production by flow cytometry. On primed-naive CD4+ T cells, the expression of regulatory T cell markers was evaluated and their suppressive ability was assessed in autologous co-cultures with CD4+ effector T cells and PPD-pulsed mDCs. We detected that memory CD4+ T cells primed by MPLA-tDCs presented reduced proliferation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in response to PPD and were refractory to subsequent stimulation. Naive CD4+ T cells were instructed by MPLA-tDCs to be hyporesponsive to antigen-specific restimulation and to suppress the induction of T helper cell type 1 and 17 responses. In conclusion, MPLA-tDCs are able to modulate antigen-specific responses of both naive and memory CD4+ T cells and might be a promising strategy to "turn off" self-reactive CD4+ effector T cells in autoimmunity.
Keywords: hyporesponsiveness; immunotherapy; memory CD4+ T cells; monocyte-derived dendritic cells; naive CD4+ T cells; tolerance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment with Dexamethasone and Monophosphoryl Lipid A Removes Disease-Associated Transcriptional Signatures in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Confers Tolerogenic Features.Front Immunol. 2016 Oct 25;7:458. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00458. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27826300 Free PMC article.
-
A short protocol using dexamethasone and monophosphoryl lipid A generates tolerogenic dendritic cells that display a potent migratory capacity to lymphoid chemokines.J Transl Med. 2013 May 24;11:128. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-128. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23706017 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells generated with different immunosuppressive cytokines induce antigen-specific anergy and regulatory properties in memory CD4+ T cells.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 15;184(4):1765-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902133. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20083662
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hyporesponsive CD4(+) T Cells in Autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 22;6:488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00488. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26441992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerance through Education: How Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Shape Immunity.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 11;8:1764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01764. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29375543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Matured Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Effectively Inhibit Autoantigen Specific CD4+ T Cells in a Murine Arthritis Model.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 28;10:2068. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02068. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555285 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis for Studies on Immunopathogenesis and Preclinical Testing of Cell-Based Therapies.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00203. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30837986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: Fine-Tuning of Dendritic Cells Function.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01232. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexamethasone and Monophosphoryl Lipid A Induce a Distinctive Profile on Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells through Transcriptional Modulation of Genes Associated With Essential Processes of the Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 23;8:1350. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01350. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29109727 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells by Endogenous Biomolecules: An Update.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 26;9:2482. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02482. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30416505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glück T, Kiefmann B, Grohmann M, Falk W, Straub RH, Schölmerich J. Immune status and risk for infection in patients receiving chronic immunosuppressive therapy. J Rheumatol (2005) 32(8):1473–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

