Gelatin sponge microparticles for the treatment of the spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage
- PMID: 27698712
- PMCID: PMC5038454
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3573
Gelatin sponge microparticles for the treatment of the spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage
Abstract
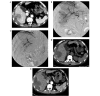
Spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage is life-threatening. The aim of the present study was to retrospectively analyze the effect of gelatin sponge microparticles (GSMs) of various diameters on the treatment of spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage. GSMs serve as embolization agents by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), and the current study analyzed their safety and efficacy. Data from a total of 13 cases of spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage, who were treated with GSM-TACE at the Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University (Dalian, China) between August 2010 and June 2014, were collected. Post-operative complications were classified according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria. Review computed tomography was conducted 1, 3 and 6 months after GSM-TACE treatment in order to determine the occurrence of re-bleeding; the tumor response was evaluated based on the Modified Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors and the expression levels of α-feroprotein. The patients were followed-up for 1-6 months (average, 5.15±1.67 months). Following GSM-TACE treatment, 13 cases reached successful hemostasis without technical complications. The survival rates 1, 3 and 6 months after treatment were 76.9 (10/13), 61.5 (8/13) and 53.8% (7/13), respectively; the objective response rates were 61.6, 53.9 and 38.5%, respectively. The primary post-operative complications were pain (100%), nausea and vomiting (69.2%), and fever (53.8%). Among the 13 patients, 2 cases underwent surgical excision 10 and 30 days after GSM-TACE, and 1 case experienced re-bleeding 3 months after treatment, after which the patient received a second treatment with TACE and successful achieved hemostasis. In conclusion, GSM-TACE of various diameters is a safe and effective method in the treatment of spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma hemorrhage. GSM-TACE is able to achieve immediate hemostasis and improves the survival rate of patients, thus creating favorable conditions for follow-up treatment.
Keywords: embolization; gelatin sponge microparticles; hepatectomy; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis; spontaneous rupture; survival; therapeutic.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
