C1 inhibitor-mediated myocardial protection from chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced injury
- PMID: 27698713
- PMCID: PMC5038163
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3592
C1 inhibitor-mediated myocardial protection from chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced injury
Abstract
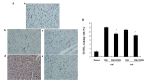
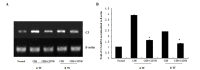
The optimal treatment for chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-induced cardiovascular injuries has yet to be determined. The aim of the current study was to explore the potential protective effect and mechanism of a C1 inhibitor in CIH in the myocardium. The present study used a rat model of CIH in which complement regulatory protein, known as C1 inhibitor (C1INH), was administered to the rats in the intervention groups. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis was detected by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling. The expression of proteins associated with the apoptotic pathway, such as B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), Bax and caspase-3 were detected by western blot analysis. The expression of complement C3 protein and RNA were also analyzed. C1INH was observed to improve the cardiac function in rats with CIH. Myocardial myeloperoxidase activity, a marker of neutrophil infiltration, was significantly decreased in the C1INH intervention group compared with the CIH control group, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis was significantly attenuated (P<0.05). Western blotting and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis indicated that the protein expression levels of Bcl-2 were decreased and those of Bax were increased in the CIH group compared with the normal control group, but the protein expression levels of Bcl-2 were increased and those of Bax were decreased in the C1INH intervention group, as compared with the CIH group. Furthermore, the CIH-induced expression and synthesis of complement C3 in the myocardium were also reduced in the C1INH intervention group. C1INH, in addition to inhibiting complement activation and inflammation, preserved cardiac function in CIH-mediated myocardial cell injury through an anti-apoptotic mechanism.
Keywords: C1 inhibitor; apoptosis; cardiomyocyte; chronic intermittent hypoxia; complement.
Figures


References
-
- Beaudin AE, Pun M, Yang C, Nicholl DD, Steinback CD, Slater DM, Edwards KE Wynne, Hanly PJ, Ahmed SB, Poulin MJ. Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 differentially regulate blood pressure and cerebrovascular responses to acute and chronic intermittent hypoxia: Implications for sleep apnea. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3:e000875. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.000875. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
