C/ EBP β mRNA expression is upregulated and positively correlated with the expression of TNIP1/ TNFAIP3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 27698734
- PMCID: PMC5038459
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3612
C/ EBP β mRNA expression is upregulated and positively correlated with the expression of TNIP1/ TNFAIP3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
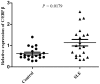
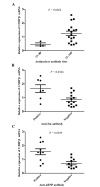
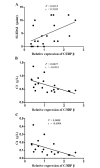
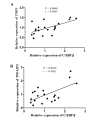
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBP β) has important roles in numerous signaling pathways. The expression of the majority of regulators and target gene products of C/EBP β, including tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) and TNFAIP3-interacting protein 1 (TNIP1), are upregulated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The aim of the present study was to investigate whether C/EBP β expression is associated with SLE pathogenesis and correlates with TNIP1 and TNFAIP3 expression. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis was used to assess the expression of C/EBP β, TNIP1, and TNFAIP3 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 20 patients with SLE and 20 healthy controls. Spearman's rank test was used to determine the correlation between C/EBP β expression and SLE disease activity, and that between C/EBP β expression and TNIP1/TNFAIP3 expression in PBMCs from patients with SLE. C/EBP β mRNA expression was markedly increased in patients with SLE compared with healthy controls. The expression of C/EBP β was positively correlated with the SLE disease activity index and negatively correlated with the serum level of complement components C3 and C4. In addition, C/EBP β mRNA expression was increased in PBMCs from SLE patients that were positive for antinuclear, anti-Smith and anti-nRNP antibodies, compared with the antibody negative SLE patients. Furthermore, the mRNA expression levels of C/EBP β in patients with SLE was positively correlated with TNIP1 and TNFAIP3 expression. The results of the current study suggest that the increased expression of C/EBP β in PBMCs and the interaction between C/EBP β and TNIP1/TNFAIP3 may be involved in the pathogenesis of SLE.
Keywords: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β; systemic lupus erythematosus; tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 3; tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 3-interacting protein 1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of the C/EBP β LAP isoform could be due to decreased TNFAIP3/TNIP1 expression in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Mod Rheumatol. 2017 Jul;27(4):657-663. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2016.1232331. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Mod Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27659348
-
Association of TNFAIP3 interacting protein 1, TNIP1 with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population: a case-control association study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R174. doi: 10.1186/ar3134. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20849588 Free PMC article.
-
Association of TNFAIP3 and TNIP1 polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus risk: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2018 Aug 20;668:155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.062. Epub 2018 May 18. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29783072
-
Anti-interferon alpha treatment in SLE.Clin Immunol. 2013 Sep;148(3):303-12. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.02.013. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23566912 Review.
-
The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the potential associations with the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Jul;42(7):1885-1896. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06560-5. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36862342 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factors in the Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis and Their Targeted Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 16;25(2):1084. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021084. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of CEBPB Attenuates Lupus Nephritis via Regulating Pim-1 Signaling.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Sep 20;2022:2298865. doi: 10.1155/2022/2298865. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36248187 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
