Protective effects of dexmedetomidine combined with flurbiprofen axetil on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27698764
- PMCID: PMC5038600
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3687
Protective effects of dexmedetomidine combined with flurbiprofen axetil on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
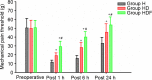
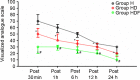
High dosages of intra-operative remifentanil are associated with opioid-induced hyperalgesia (OIH). The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of combined dexmedetomidine and flurbiprofen axetil treatment on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia. Patients with an American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status of I-II who were diagnosed with hysteromyoma and scheduled for laparoscopic assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH) were randomly divided into three groups. Group hyperalgesia (Group H, n=29) received intra-operative remifentanil, Group hyperalgesia and dexmedetomidine (Group HD, n=28) received remifentanil and a continuous infusion of dexmedetomidine, and Group hyperalgesia, dexmedetomidine and flurbiprofen axetil (Group HDF, n=29) received remifentanil, flurbiprofen axetil and dexmedetomidine. Mechanical pain thresholds were measured during the preoperative visit and postoperatively at 1, 6 and 24-h time points. Visual analog scale (VAS) scores, time to analgesic requirement, total sufentanil consumption and side effects were assessed postoperatively. Mechanical pain threshold at the incision site was significantly lower in Group H compared with Groups HD and HDF (both P<0.05), and significantly higher in Group HDF than in Group HD (P<0.05). The area of secondary hyperalgesia at the incision site was greater in Group H than in the other two groups (both P<0.05), and significantly smaller in Group HDF compared with Group HD (P<0.05). VAS scores and total sufentanil consumption were significantly higher in Group H compared with the other two groups (both P<0.05), and were significantly lower in Group HDF compared with Group HD (P<0.05). Dexmedetomidine combined with flurbiprofen axetil exhibits synergetic effects in the prevention of remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia in patients undergoing LAVH.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine; flurbiprofen axetil; opioid induced hyperalgesia; remifentanil.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preoperative butorphanol and flurbiprofen axetil therapy attenuates remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia after laparoscopic gynaecological surgery: a randomized double-blind controlled trial.Br J Anaesth. 2016 Oct;117(4):504-511. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew248. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Br J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 28077539 Clinical Trial.
-
Antihyperalgesic effects of dexmedetomidine on high-dose remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013 Apr;64(4):301-7. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2013.64.4.301. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013. PMID: 23646238 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative But Not Postoperative Flurbiprofen Axetil Alleviates Remifentanil-induced Hyperalgesia After Laparoscopic Gynecological Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-blinded, Trial.Clin J Pain. 2017 May;33(5):435-442. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000416. Clin J Pain. 2017. PMID: 27518488 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine and Remifentanil in Reducing Postoperative Pain and Opioid Use: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Feb 27;17(2):e79759. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79759. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40028430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological interventions for preventing opioid-induced hyperalgesia in adults after opioid-based anesthesia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1199794. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1199794. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37426819 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of an intraoperative intravenous Bolus Dose of Dexmedetomidine on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in male patients undergoing transurethral resection of bladder tumors: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;80(3):465-474. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03625-5. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38216655 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes of Entropy Index and Cerebral Oxygen Metabolism in the Maintenance of Remifentanil Anesthesia and Their Predictive Value for Postoperative Hyperalgesia.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 11;2022:1080858. doi: 10.1155/2022/1080858. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9840276. doi: 10.1155/2023/9840276. PMID: 35309843 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
New Perspective for Drug-Drug Interaction in Perioperative Period.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 21;12(14):4810. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144810. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37510925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks of the abdominal wall on pain relief after laparoscopic cholecystectomy.J Pain Res. 2019 May 3;12:1433-1439. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S203721. eCollection 2019. J Pain Res. 2019. PMID: 31118761 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of dexmedetomidine on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia and the sex differences.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3596-3602. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6641. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30233714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee M, Silverman SM, Hansen H, Patel VB, Manchikanti L. A comprehensive review of opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Pain Physician. 2011;14:145–161. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
