Role of Yes-associated protein in cancer: An update
- PMID: 27698789
- PMCID: PMC5038596
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4955
Role of Yes-associated protein in cancer: An update
Abstract
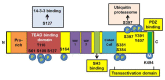
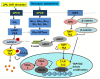
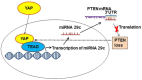
Yes-associated protein (YAP) is an oncoprotein located in the cytoplasm in an inactive form, and when activated, it translocates to the nucleus and activates the transcription of genes responsible for cell division and apoptosis. YAP is one of the downstream regulatory proteins in the Hippo signaling pathway, which is important in cell proliferation and regeneration. Due to its great importance, YAP is regulated very strictly by different regulatory systems. The present review will focus on the canonical pathways of YAP, and will provide details on the most recent findings regarding its regulation and role in tumorigenesis, specifically in prostate tumor progression.
Keywords: YAP; cancer; prostate cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi R, Hall RA, Donowitz M, Hisaminato A, Fujiwara T, Ito Y, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB. TAZ: A novel transcriptional co-activator regulated by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J. 2000;19:6778–6791. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6778. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shimomura T, Miyamura N, Hata S, Miura R, Hirayama J, Nishina H. The PDZ-binding motif of Yes-associated protein is required for its co-activation of TEAD-mediated CTGF transcription and oncogenic cell transforming activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;17:917–931. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.100. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
