Anti-cancer effect of ursolic acid activates apoptosis through ROCK/PTEN mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 in prostate cancer
- PMID: 27698874
- PMCID: PMC5038386
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5015
Anti-cancer effect of ursolic acid activates apoptosis through ROCK/PTEN mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 in prostate cancer
Abstract
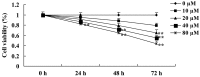
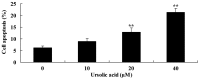
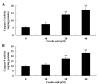
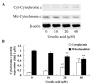
Ursolic acid is a type of pentacyclic triterpene compound with multiple pharmacological activities including cancer resistance, protection from liver injury, antisepsis, anti-inflammation and antiviral activity. The present study aimed to investigate the anticancer effect of ursolic acid. Ursolic acid activates cell apoptosis and its pro-apoptotic mechanism remains to be fully elucidated. Cell Counting kit-8 assays, flow cytometric analysis and analysis of caspase-3 and caspase-9 activity were used to estimate the anticancer effect of ursolic acid on DU145 prostate cancer cells. The protein expression of cytochrome c, rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and cofilin-1 were examined using western blot analysis. In the present study, ursolic acid significantly suppressed cell growth and induced apoptosis, as well as increasing caspase-3 and caspase-9 activities of DU145 cells. Furthermore, cytoplasmic and mitochondrial cytochrome c protein expression was significantly activated and suppressed, respectively, by ursolic acid. Ursolic acid significantly suppressed the ROCK/PTEN signaling pathway and inhibited cofilin-1 protein expression in DU145 cells. The results of the present study indicate that the anticancer effect of ursolic acid activates cell apoptosis through ROCK/PTEN mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 in prostate cancer.
Keywords: cofilin-1; cytochrome c; prostate cancer; rho-associated protein kinase/phosphatase and tensin homolog; ursolic acid.
Figures
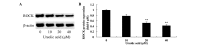
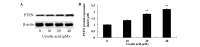
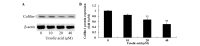
References
-
- Dossus L, Kaaks R, Canzian F, Albanes D, Berndt SI, Boeing H, Buring J, Chanock SJ, Clavel-Chapelon F, Feigelson HS, et al. PTGS2 and IL6 genetic variation and risk of breast and prostate cancer: Results from the Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium (BPC3) Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang J, Yu L, Huang X, Chen X, Li D, Zhang Y, Tang L, Zhao S. Identification of two novel human dynein light chain genes, DNLC2A and DNLC2B, and their expression changes in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues from 68 Chinese patients. Gene. 2001;281:103–113. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00787-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
