A sesquiterpene lactone from Siegesbeckia glabrescens suppresses Hedgehog/Gli-mediated transcription in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 27698879
- PMCID: PMC5038360
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4994
A sesquiterpene lactone from Siegesbeckia glabrescens suppresses Hedgehog/Gli-mediated transcription in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
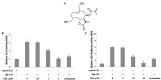
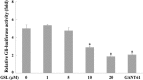
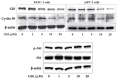
Pancreatic cancer is aggressive and therefore difficult to treat; however, continued efforts have been made with the aim of developing an effective therapy against the disease. The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is reportedly involved in the proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells. The transcription factor glioma-associated oncogene (Gli) is a key component of the Hh signaling pathway and the primary effector of pancreatic cancer development. Inhibiting Gli is a proven therapeutic strategy for this disease. The present study examined the regulation of Gli and the expression of its target genes to identify an inhibitor of the Sonic Hh (Shh) pathway. A germacranolide sesquiterpene lactone (GSL) was isolated from Siegesbeckia glabrescens as an inhibitor of Gli-mediated transcription. The results demonstrated that GSL inhibited Shh-induced osteoblast differentiation and Gli homolog 1 (Gli1)-mediated transcriptional activity in mesenchymal C3H10T1/2 stem cells. Furthermore, GSL suppressed Gli-mediated transcriptional activity in human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells, which resulted in reduced cancer cell proliferation and downregulated expression of the Gli-target genes, Gli1 and cyclin D1. A sesquiterpene lactone from S. glabrescens may therefore serve as a candidate for the treatment of Hh/Gli-dependent pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Gli; Hedgehog pathway; Siegesbeckia glabrescens; compositae; pancreatic cancer; sesquiterpene lactone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-arrestin1-mediated acetylation of Gli1 regulates Hedgehog/Gli signaling and modulates self-renewal of SHH medulloblastoma cancer stem cells.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3477-0. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28716052 Free PMC article.
-
The intrahepatic signalling niche of hedgehog is defined by primary cilia positive cells during chronic liver injury.J Hepatol. 2014 Jan;60(1):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.012. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23978713
-
Sanguinarine inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics by inducing oxidative stress and suppressing sonic hedgehog-Gli-Nanog pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Oct 1;38(10):1047-1056. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx070. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28968696
-
The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Feb 20;18(1):8-20. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2018.2756. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29274272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-Generation Hedgehog/GLI Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 15;11(4):538. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040538. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30991683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dauricine suppresses the growth of pancreatic cancer in vivo by modulating the Hedgehog signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4403-4414. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10790. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611949 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hedgehog Signaling in Cancer by Natural and Dietary Compounds.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018 Jan;62(1):10.1002/mnfr.201700621. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700621. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2018. PMID: 29164817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers, and targeted therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Aug 18;8(1):315. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01559-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37596267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesquiterpene Lactones as Promising Candidates for Cancer Therapy: Focus on Pancreatic Cancer.Molecules. 2022 May 29;27(11):3492. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113492. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rab23 promotes the cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer via the Shh-Gli-ABCG2 signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5155-5160. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.7949. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo J, Gao J, Li Z, Gong Y, Man X, Jin J, Wu H. Adenovirus vector-mediated Gli1 siRNA induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer with Smo-dependent or Smo-independent Hh pathway activation in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2013;339:185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hao K, Tian XD, Qin CF, Xie XH, Yang YM. Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates human pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:1124–1132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
