MicroRNA-20b (miR-20b) Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tumorigenicity in Esophageal Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Expression
- PMID: 27701465
- PMCID: PMC5049758
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164105
MicroRNA-20b (miR-20b) Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tumorigenicity in Esophageal Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Expression
Retraction in
-
Retraction: MicroRNA-20b (miR-20b) Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tumorigenicity in Esophageal Cancer Cells via the Regulation of Phosphatase and Tensin Homologue Expression.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 19;17(1):e0262879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262879. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35045131 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
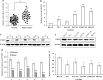
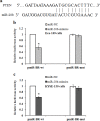
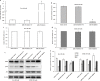
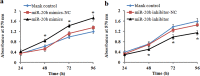
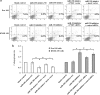
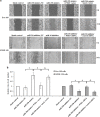
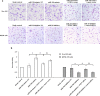
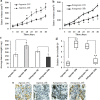
Increasing evidence has indicated that many microRNAs participate in the development and progression of esophageal cancer and gene expression regulation. MicroRNA-20b (miR-20b) has been reported to be aberrantly expressed in various cancers, but its exact role in esophageal cancer cells remains unclear so far. Therefore, we detected the levels of miR-20b in esophageal tumor tissues and their adjacent normal tissues, and various esophageal cancer cell lines by qRT-PCR. We also explored the effects of miR-20b on cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumorigenicity of esophageal carcinoma cells through transfection with miR-20b mimics or inhibitor to upregulate or downregulate miR-20b expression in the esophageal cancer cells Eca-109 and KYSE-150, respectively. Additionally, the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) binding with miR-20b was analyzed by dual-luciferase reporter assays. The results indicated that miR-20b expression level in esophageal tumor tissues was significantly increased compared with their neighboring normal tissues, but its expression was inverse with PTEN protein expression. Luciferase assays confirmed that the 3'-UTR of PTEN was a target of miR-20b in esophageal cancer cells. MiR-20b upregulation promoted cell proliferation, migration, invasiveness, and tumor growth, and decreased apoptosis, and reduced PTEN protein level but not mRNA expression in Eca-109 cells. Conversely, downregulation of miR-20b suppressed these processes in KYSE-150 cells, and enhanced PTEN protein expression. These data indicate that miR-20b plays important roles in tumorigenesis of esophageal cancer possibly via regulation of PTEN expression, and it may be a potential therapeutic target for esophageal cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Li JC, Liu D, Yang Y, Wang XY, Pan DL, Qiu ZD, et al. Growth, clonability, and radiation resistance of esophageal-derived stem-like cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14: 4891–4896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

