Identification of Neutrophil Exocytosis Inhibitors (Nexinhibs), Small Molecule Inhibitors of Neutrophil Exocytosis and Inflammation: DRUGGABILITY OF THE SMALL GTPase Rab27a
- PMID: 27702998
- PMCID: PMC5207069
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.741884
Identification of Neutrophil Exocytosis Inhibitors (Nexinhibs), Small Molecule Inhibitors of Neutrophil Exocytosis and Inflammation: DRUGGABILITY OF THE SMALL GTPase Rab27a
Abstract
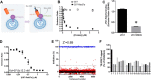
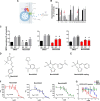
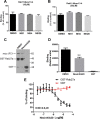
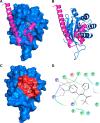
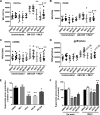
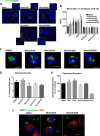
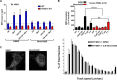
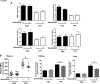
Neutrophils constitute the first line of cellular defense in response to bacterial and fungal infections and rely on granular proteins to kill microorganisms, but uncontrolled secretion of neutrophil cargos is injurious to the host and should be closely regulated. Thus, increased plasma levels of neutrophil secretory proteins, including myeloperoxidase and elastase, are associated with tissue damage and are hallmarks of systemic inflammation. Here, we describe a novel high-throughput screening approach to identify small molecule inhibitors of the interaction between the small GTPase Rab27a and its effector JFC1, two central regulators of neutrophil exocytosis. Using this assay, we have identified small molecule inhibitors of Rab27a-JFC1 binding that were also active in cell-based neutrophil-specific exocytosis assays, demonstrating the druggability of Rab GTPases and their effectors. These compounds, named Nexinhibs (neutrophil exocytosis inhibitors), inhibit exocytosis of azurophilic granules in human neutrophils without affecting other important innate immune responses, including phagocytosis and neutrophil extracellular trap production. Furthermore, the compounds are reversible and potent inhibitors of the extracellular production of superoxide anion by preventing the up-regulation of the granule membrane-associated subunit of the NADPH oxidase at the plasma membrane. Nexinhibs also inhibit the up-regulation of activation signature molecules, including the adhesion molecules CD11b and CD66b. Importantly, by using a mouse model of endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation, we show that these inhibitors have significant activity in vivo manifested by decreased plasma levels of neutrophil secretory proteins and significantly decreased tissue infiltration by inflammatory neutrophils. Altogether, our data present the first neutrophil exocytosis-specific inhibitor with in vivo anti-inflammatory activity, supporting its potential use as an inhibitor of systemic inflammation.
Keywords: JFC1; Rab27a GTPases and effectors; druggability of GTPases; exocytosis; inflammation; inhibitor; innate immunity; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); neutrophil; systemic inflammation.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rab27a and Rab27b regulate neutrophil azurophilic granule exocytosis and NADPH oxidase activity by independent mechanisms.Traffic. 2010 Apr;11(4):533-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01029.x. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20028487 Free PMC article.
-
Nexinhib20 inhibits JFC1-mediated mobilization of a subset of CD11b/CD18+ vesicles decreasing integrin avidity, but does not inhibit Rac1.J Leukoc Biol. 2025 Apr 23;117(4):qiaf012. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiaf012. J Leukoc Biol. 2025. PMID: 39883854 Free PMC article.
-
The Rab27a effectors JFC1/Slp1 and Munc13-4 regulate exocytosis of neutrophil granules.Traffic. 2008 Dec;9(12):2151-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00838.x. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18939952 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating secretory organelles and endosomes in neutrophils and their implications for inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2016 Sep;273(1):249-65. doi: 10.1111/imr.12452. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27558339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Rab27a in the regulation of neutrophil function.Cell Microbiol. 2014 Sep;16(9):1301-10. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12328. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Cell Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24964030 Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of Exosomal PD-L1 in Cancer Progression and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target.Cells. 2021 Nov 19;10(11):3247. doi: 10.3390/cells10113247. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecules that inhibit the late stage of Munc13-4-dependent secretory granule exocytosis in mast cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 25;293(21):8217-8229. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001547. Epub 2018 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29615494 Free PMC article.
-
RAB27B controls palmitoylation-dependent NRAS trafficking and signaling in myeloid leukemia.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jun 15;133(12):e165510. doi: 10.1172/JCI165510. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37317963 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the RAB27/SYTL Axis in Tumor Microenvironment Construction.Cancer Sci. 2025 Jul;116(7):1815-1822. doi: 10.1111/cas.70096. Epub 2025 May 4. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 40319893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From rough to precise: PD-L1 evaluation for predicting the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockades.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 3;13:920021. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.920021. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35990664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mantovani A., Cassatella M. A., Costantini C., and Jaillon S. (2011) Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 519–531 - PubMed
-
- Lee W. L., Harrison R. E., and Grinstein S. (2003) Phagocytosis by neutrophils. Microbes Infect. 5, 1299–1306 - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V., Reichard U., Goosmann C., Fauler B., Uhlemann Y., Weiss D. S., Weinrauch Y., and Zychlinsky A. (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303, 1532–1535 - PubMed
-
- Amulic B., Cazalet C., Hayes G. L., Metzler K. D., and Zychlinsky A. (2012) Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 30, 459–489 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

