Treatment of Hypertension with Combination of Lisinopril/Hydrochlorothiazide
- PMID: 27703294
- PMCID: PMC5034990
- DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2016.70.299-302
Treatment of Hypertension with Combination of Lisinopril/Hydrochlorothiazide
Abstract
Introduction: Paper is written on the basis of data collected in collaboration with family doctors in several cities in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Material and methods: In this retrospective, randomized study was carried out processing of data collected by special design questionnaire from the field through studies and analyzes carried out in 5 health care institutions in the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The study included 270 patients who underwent three consecutive medical examinations.
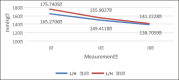
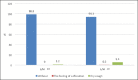
Results: Total reduction in blood pressure in average was 32.8 mmHg for systolic and 17.1 mmHg for diastolic, which is consistent with previously published results. Lisinopril/Hydrochlorothiazide is therefore a valuable therapy in the field of internal medicine. Study of this medication confirmed its efficacy in the treatment of hypertension.
Conclusion: Control of high blood pressure in our patients according to data was very low, so it is necessary to intensify measures of prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide; hypertension; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
• Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures
References
-
- Antihypertensives effectiveness of low-dose Lisinopril-hydrochlorothiazide combination. A large multicenter study. Lisinopril-Hydrochlorothiazide Group., Chrysant SG. Arch-Intern-Med. 1994 Apr 11;154(7):737–43. - PubMed
-
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors enhance the antihypertensives efficacy of diuretics and blunt or prevent adverse metabolic effects. Weinberger MH. 1989. J. Cardiovascular. Pharmacol. 13:S1–S4. - PubMed
-
- Patlak M. “From viper's venom to drug design: treating hypertension”. FASEB J. 2004 Mar;18(3):421. - PubMed
-
- Katzung Bertram. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Vol. 175. New York City, New York: McGraw Hill; 2012. pp. 184–185.
-
- Drug Information for the Health Care Professional (USP DI) (2001): Lisinopril. (21th ed) I:171–179.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical