Clinical, pathological, and radiological characteristics of solitary ground-glass opacity lung nodules on high-resolution computed tomography
- PMID: 27703366
- PMCID: PMC5036641
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S110363
Clinical, pathological, and radiological characteristics of solitary ground-glass opacity lung nodules on high-resolution computed tomography
Abstract
Background: Lung nodules are being detected at an increasing rate year by year with high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) being widely used. Ground-glass opacity nodule is one of the special types of pulmonary nodules that is confirmed to be closely associated with early stage of lung cancer. Very little is known about solitary ground-glass opacity nodules (SGGNs). In this study, we analyzed the clinical, pathological, and radiological characteristics of SGGNs on HRCT.
Methods: A total of 95 resected SGGNs were evaluated with HRCT scan. The clinical, pathological, and radiological characteristics of these cases were analyzed.
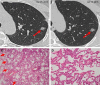
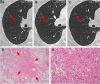
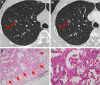
Results: Eighty-one adenocarcinoma and 14 benign nodules were observed. The nodules included 12 (15%) adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), 14 (17%) minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), and 55 (68%) invasive adenocarcinoma (IA). No patients with recurrence till date have been identified. The positive expression rates of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and ROS-1 (proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS) were only 2.5% and 8.6%, respectively. The specificity and accuracy of HRCT of invasive lung adenocarcinoma were 85.2% and 87.4%. The standard uptake values of only two patients determined by 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) were above 2.5. The size, density, shape, and pleural tag of nodules were significant factors that differentiated IA from AIS and MIA. Moreover, the size, shape, margin, pleural tag, vascular cluster, bubble-like sign, and air bronchogram of nodules were significant determinants for mixed ground-glass opacity nodules (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: We analyzed the clinical, pathological, and radiological characteristics of SGGNs on HRCT and found that the size, density, shape, and pleural tag of SGGNs on HRCT are found to be the determinant factors of IA. In conclusion, detection of anaplastic lymphoma kinase expression and performance of PET/CT scan are not routinely recommended.
Keywords: HRCT; SGGNs; adenocarcinoma; clinical; pathological.
Figures
References
-
- Austin JH, Muller NL, Friedman PJ, et al. Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 1996;200(2):327–331. - PubMed
-
- Collins J, Stern EJ. Ground-glass opacity at CT: the ABCs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169(2):355–367. - PubMed
-
- Lee HY, Lee KS. Ground-glass opacity nodules: histopathology, imaging evaluation, and clinical implications. J Thorac Imaging. 2011;26(2):106–118. - PubMed
-
- Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Mirtcheva R, et al. CT screening for lung cancer: frequency and significance of part-solid and nonsolid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(5):1053–1057. - PubMed
-
- Lim HJ, Ahn S, Lee KS, et al. Persistent pure ground-glass opacity lung nodules ≥10 mm in diameter at CT scan: histopathologic comparisons and prognostic implications. Chest. 2013;144(4):1291–1299. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

