Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators in cystic fibrosis: current perspectives
- PMID: 27703398
- PMCID: PMC5036583
- DOI: 10.2147/CPAA.S100759
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators in cystic fibrosis: current perspectives
Abstract
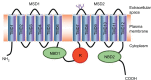
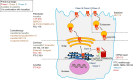
Mutations of the CFTR gene cause cystic fibrosis (CF), the most common recessive monogenic disease worldwide. These mutations alter the synthesis, processing, function, or half-life of CFTR, the main chloride channel expressed in the apical membrane of epithelial cells in the airway, intestine, pancreas, and reproductive tract. Lung disease is the most critical manifestation of CF. It is characterized by airway obstruction, infection, and inflammation that lead to fatal tissue destruction. In spite of great advances in early and multidisciplinary medical care, and in our understanding of the pathophysiology, CF is still considerably reducing the life expectancy of patients. This review highlights the current development in pharmacological modulators of CFTR, which aim at rescuing the expression and/or function of mutated CFTR. While only Kalydeco® and Orkambi® are currently available to patients, many other families of CFTR modulators are undergoing preclinical and clinical investigations. Drug repositioning and personalized medicine are particularly detailed in this review as they represent the most promising strategies for restoring CFTR function in CF.
Keywords: correctors; drug repositioning; high-throughput screening; personalized medicine; potentiators; precision medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Riordan J, Rommens J, Kerem B, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989;245(4922):1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Marcorelles P, Friocourt G, Uguen A, Ledé F, Férec C, Laquerrière A. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) expression in the developing human brain: comparative immunohistochemical study between patients with normal and mutated CFTR. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014;62(11):791–801. - PubMed
-
- Gao Z, Sun HY, Lau CP, Chin-Wan Fung P, Li GR. Evidence for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride current in swine ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42(1):98–105. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

