TACC3 overexpression in cholangiocarcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and is a potential anti-cancer molecular drug target for HDAC inhibitors
- PMID: 27705912
- PMCID: PMC5342751
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12254
TACC3 overexpression in cholangiocarcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and is a potential anti-cancer molecular drug target for HDAC inhibitors
Abstract
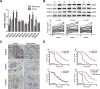
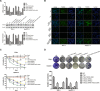
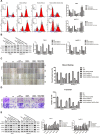
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) have been implicated in multiple malignant tumors, and HDAC inhibitors (HDACIs) exert anti-cancer effects. However, the expression of HDACs and the anti-tumor mechanism of HDACIs in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) have not yet been elucidated. In this study, we found that expression of HDACs 2, 3, and 8 were up-regulated in CCA tissues and those patients with high expression of HDAC2 and/or HDAC3 had a worse prognosis. In CCA cells, two HDACIs, trichostatin (TSA) and vorinostat (SAHA), suppressed proliferation and induced apoptosis and G2/M cycle arrest. Microarray analysis revealed that TACC3 mRNA was down-regulated in CCA cells treated with TSA. TACC3 was highly expressed in CCA tissues and predicted a poor prognosis in CCA patients. TACC3 knockdown induced G2/M cycle arrest and suppressed the invasion, metastasis, and proliferation of CCA cells, both in vitro and in vivo. TACC3 overexpression reversed the effects of its knockdown. These findings suggest TACC3 may be a useful prognostic biomarker for CCA and is a potential therapeutic target for HDACIs.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitors (HDACIs); cholangiocarcinoma (CCA); histone deacetylase (HDAC); microarray; transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 3 (TACC3).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Contribution of Histone Deacetylases in Prognosis and Therapeutic Management of Cholangiocarcinoma.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Apr;24(2):175-184. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00454-x. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32125662 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase 3 overexpression in human cholangiocarcinoma and promotion of cell growth via apoptosis inhibition.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 1;8(6):e2856. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.457. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569784 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors as potential therapeutic drugs for cholangiocarcinoma - cell line findings.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(4):2503-8. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.4.2503. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23725164
-
Changes in histone deacetylase (HDAC) expression patterns and activity of HDAC inhibitors in urothelial cancers.Urol Oncol. 2013 Nov;31(8):1770-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22944197
-
New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jan;124(1):30-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI69738. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24382387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primary Cilia, Ciliogenesis and the Actin Cytoskeleton: A Little Less Resorption, A Little More Actin Please.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 17;8:622822. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.622822. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33392209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TACC3 transcriptionally upregulates E2F1 to promote cell growth and confer sensitivity to cisplatin in bladder cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 22;9(2):72. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0112-6. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29358577 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of TACC3 Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Human Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells.Oncol Res. 2018 Mar 5;26(2):183-189. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14837020772250. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28109075 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Histone Deacetylases in Prognosis and Therapeutic Management of Cholangiocarcinoma.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Apr;24(2):175-184. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00454-x. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32125662 Review.
-
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Promising Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Thymic Epithelial Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4263. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054263. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patt YZ, Hassan MM, Lozano RD, Waugh KA, Hoque AM, Frome AI, Lahoti S, Ellis L, Vauthey JN, Curley SA, Schnirer, Raijman I. Phase II trial of cisplatin, interferon alpha-2b, doxorubicin, and 5-fluorouracil for biliary tract cancer. Clinical cancer research. 2001;7:3375–3380. - PubMed
-
- Martin R, Jarnagin W. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Current management. Minerva Chir. 2003;58:469–478. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

