Controlling Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) in Haiti: Implementation Strategies and Evidence of Their Success
- PMID: 27706162
- PMCID: PMC5051938
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004954
Controlling Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) in Haiti: Implementation Strategies and Evidence of Their Success
Abstract
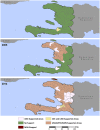
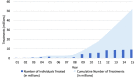
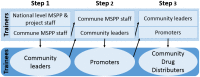
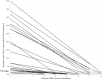
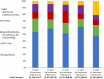
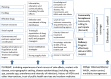
Lymphatic filariasis (LF) and soil-transmitted helminths (STH) have been targeted since 2000 in Haiti, with a strong mass drug administration (MDA) program led by the Ministry of Public Health and Population and its collaborating international partners. By 2012, Haiti's neglected tropical disease (NTD) program had reached full national scale, and with such consistently good epidemiological coverage that it is now able to stop treatment for LF throughout almost all of the country. Essential to this success have been in the detail of how MDAs were implemented. These key programmatic elements included ensuring strong community awareness through an evidence-based, multi-channel communication and education campaign facilitated by voluntary drug distributors; strengthening community trust of the drug distributors by ensuring that respected community members were recruited and received appropriate training, supervision, identification, and motivation; enforcing a "directly observed treatment" strategy; providing easy access to treatment though numerous distribution posts and a strong drug supply chain; and ensuring quality data collection that was used to guide and inform MDA strategies. The evidence that these strategies were effective lies in both the high treatment coverage obtained- 100% geographical coverage reached in 2012, with almost all districts consistently achieving well above the epidemiological coverage targets of 65% for LF and 75% for STH-and the significant reduction in burden of infection- 45 communes having reached the target threshold for stopping treatment for LF. By taking advantage of sustained international financial and technical support, especially during the past eight years, Haiti's very successful MDA campaign resulted in steady progress toward LF elimination and development of a strong foundation for ongoing STH control. These efforts, as described, have not only helped establish the global portfolio of "best practices" for NTD control but also are poised to help solve two of the most important future NTD challenges-how to maintain control of STH infections after the community-based LF "treatment platform" ceases and how to ensure appropriate morbidity management for patients currently suffering from lymphatic filarial disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partnering for impact: Integrated transmission assessment surveys for lymphatic filariasis, soil transmitted helminths and malaria in Haiti.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Feb 16;11(2):e0005387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005387. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28207792 Free PMC article.
-
Costs of integrated mass drug administration for neglected tropical diseases in Haiti.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011 Nov;85(5):826-33. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0635. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011. PMID: 22049035 Free PMC article.
-
Endpoints for lymphatic filariasis programs.Emerg Infect Dis. 2007 Apr;13(4):608-10. doi: 10.3201/eid1304.061063. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17553278 Free PMC article.
-
Progress towards control and elimination of neglected tropical diseases targeted by preventive chemotherapy in São Tomé e Príncipe.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022 May 2;116(5):446-453. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trab153. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 34718820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the elimination of lymphatic filariasis by 2020: treatment update and impact assessment for the endgame.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013 Jul;11(7):723-31. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2013.811841. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013. PMID: 23879610 Review.
Cited by
-
"Our desire is to make this village intestinal worm free": Identifying determinants of high coverage of community-wide mass drug administration for soil transmitted helminths in Benin, India, and Malawi.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Feb 6;18(2):e0011819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011819. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38319937 Free PMC article.
-
Neglected tropical diseases in Europe: an emerging problem for health professionals.Intern Emerg Med. 2017 Jun;12(4):423-424. doi: 10.1007/s11739-017-1648-2. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Intern Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 28315147 No abstract available.
-
Eliminating Cholera Transmission in Haiti.N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 12;376(2):101-103. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1614104. Epub 2016 Dec 7. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 27959699 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Use of lay vaccinators in animal vaccination programmes: A scoping review.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Aug 10;15(8):e0009691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009691. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34375325 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating context-specific evidence-based quality improvement intervention on lymphatic filariasis mass drug administration in Northern Ghana using the RE-AIM framework.Trop Med Health. 2021 Feb 18;49(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s41182-021-00305-3. Trop Med Health. 2021. PMID: 33602322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (2012) Accelerating work to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases—A roadmap for implementation. Switzerland: WHO.
-
- WHO (2014) Lyphatic filariasis Fact Sheet. WHO.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

