Involvement of the NLRC4-Inflammasome in Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 27706238
- PMCID: PMC5051905
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164135
Involvement of the NLRC4-Inflammasome in Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
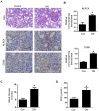
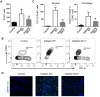
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease worldwide but current treatments remain suboptimal. The role of inflammation in DN has only recently been recognized. It has been shown that the NLRP3-inflammasome contributes to DN development by inducing interleukin (IL)-1β processing and secretion. In an effort to understand other IL-1β activating mechanism during DN development, we examined the role of the NLRC4-inflammasome in DN and found that NLRC4 is a parallel mechanism, in addition to the NLRP3-inflammasome, to induce pro-IL-1β processing and activation. We found that the expression of NLRC4 is elevated in DN kidneys. NLRC4-deficiency results in diminished DN disease progression, as manifested by a decrease in blood glucose and albumin excretion, as well as preserved renal histology. We further found that DN kidneys have increased F4/80+ macrophages, increased IL-1β production, and other signaling pathways related to kidney pathology such as activation of NF-κB and MAP kinase pathways, all of which were rescued by NLRC4-deficiency. This study demonstrates NLRC4-driven IL-1β production as critical for the progression of DN, which underscores the importance to target this pathway to alleviate this devastating disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hyperuricemia-induced NLRP3 activation of macrophages contributes to the progression of diabetic nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 May 1;308(9):F993-F1003. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00637.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25651569
-
Nlrc4 Inflammasome Expression After Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 14;26(8):3697. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083697. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332346 Free PMC article.
-
The Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 subverts human NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasome responses.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Feb;105(2):401-410. doi: 10.1002/JLB.MA0318-112RR. Epub 2018 Oct 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30368901
-
The NAIP-NLRC4 inflammasome in innate immune detection of bacterial flagellin and type III secretion apparatus.Immunol Rev. 2015 May;265(1):85-102. doi: 10.1111/imr.12293. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25879286 Review.
-
NLRC4 inflammasomopathies.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Dec;17(6):398-404. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000396. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28957823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome participates in macrophage responses to Trypanosoma cruzi by a mechanism that relies on cathepsin-dependent caspase-1 cleavage.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 6;14:1282856. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1282856. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38124741 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingomyelin synthase 1 mediates hepatocyte pyroptosis to trigger non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Gut. 2021 Oct;70(10):1954-1964. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322509. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Gut. 2021. PMID: 33208407 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia-induced inflamm-aging accelerates gingival senescence via NLRC4 phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 6;294(49):18807-18819. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010648. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31676687 Free PMC article.
-
Effect and Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome During Renal Fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jan 24;7:379. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00379. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32039201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To Explore the Putative Molecular Targets of Diabetic Nephropathy and their Inhibition Utilizing Potential Phytocompounds.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(24):3752-3790. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230519112312. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37211853 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

