The involvement of endothelial mediators in leprosy
- PMID: 27706378
- PMCID: PMC5066329
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760160122
The involvement of endothelial mediators in leprosy
Abstract
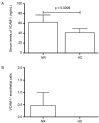
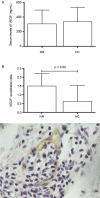
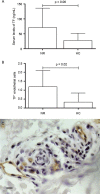
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease that requires better understanding since it continues to be a significant health problem in many parts of the world. Leprosy reactions are acute inflammatory episodes regarded as the central etiology of nerve damage in the disease. The activation of endothelium is a relevant phenomenon to be investigated in leprosy reactions. The present study evaluated the expression of endothelial factors in skin lesions and serum samples of leprosy patients. Immunohistochemical analysis of skin samples and serum measurements of VCAM-1, VEGF, tissue factor and thrombomodulin were performed in 77 leprosy patients and 12 controls. We observed significant increase of VCAM-1 circulating levels in non-reactional leprosy (p = 0.0009). The immunostaining of VEGF and tissue factor was higher in endothelium of non-reactional leprosy (p = 0.02 for both) than healthy controls. Patients with type 1 reaction presented increased thrombomodulin serum levels, compared with non-reactional leprosy (p = 0.02). In type 2 reaction, no significant modifications were observed for the endothelial factors investigated. The anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities of the endotfhelial factors may play key-roles in the pathogenesis of leprosy and should be enrolled in studies focusing on alternative targets to improve the management of leprosy and its reactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased chitotriosidase activity in serum of leprosy patients: association with bacillary leprosy.Clin Immunol. 2009 Jun;131(3):501-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.02.003. Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19307157
-
Endothelial cell activation in cutaneous vasculitis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 1996 Jan;21(1):28-32. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1996. PMID: 8689765
-
Leprosy patients: neurotrophic factors and axonal markers in skin lesions.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2012 Apr;70(4):281-6. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2012000400012. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2012. PMID: 22510739
-
Study of apoptosis in skin lesions of leprosy in relation to treatment and lepra reactions.Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 2005 Dec;73(4):269-76. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 2005. PMID: 16830636
-
Genetics of leprosy reactions: an overview.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012 Dec;107 Suppl 1:132-42. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762012000900020. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2012. PMID: 23283464 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune mediators as plasma biomarkers for identifying household contacts and classifying clinical forms and leprosy reactions.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 5;16:1513060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1513060. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40109344 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Polarization in Leprosy-HIV Co-infected Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 29;11:1493. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01493. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849508 Free PMC article.
-
Different profiles of chemokines, cytokines and cell growth factors in plasma samples from patients with leprosy, leprosy reactions and households contacts.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024 Feb 19;119:e230129. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760230129. eCollection 2024. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024. PMID: 38381878 Free PMC article.
-
miRNome Expression Analysis Reveals New Players on Leprosy Immune Physiopathology.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 9;9:463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00463. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29593724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Endothelial activation is associated with albuminuria in multibacillary leprosy.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021 Jun 18;63:e44. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202163044. eCollection 2021. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021. PMID: 34161550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aird WC. Spatial and temporal dynamics of the endothelium. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(7):1392–1406. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Vascular bed-specific hemostasis: role of endothelium in sepsis pathogenesis. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7):S28–S34. - PubMed
-
- Bode MF, Mackman N. Protective and pathological roles of tissue factor in the heart. Hamostaseologie. 2015;35(1):37–46. - PubMed
-
- Boehme MW, Nawroth PP, Kling E, Lin J, Amiral J, Riedesel J, et al. Serum thrombomodulin. A novel marker of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(4):572–577. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

