The metabolic stress response to burn trauma: current understanding and therapies
- PMID: 27707498
- PMCID: PMC5753602
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31469-6
The metabolic stress response to burn trauma: current understanding and therapies
Abstract
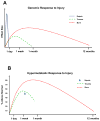
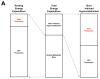
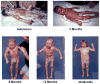
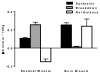
Major burns provoke a profound stress response, which is unrivalled in terms of its magnitude and duration. Evidence suggests that the pathophysiological stress response to severe burn trauma persists for several years after injury. Thus, there is a pressing need for novel strategies that mitigate this response and restore normal metabolic function in patients with burns. This is the first in a Series of three papers about the care of people with burns. In this paper, we review the current knowledge of the stress response to burn trauma, with a focus on hypermetabolism, muscle wasting, and stress-induced diabetes. We highlight recent developments and important knowledge gaps that need to be pursued to develop novel therapeutic strategies to improve outcomes in burn survivors.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflict of interest to disclose. C.P. drafted the manuscript and produced the Figures. R.G.T., L.S.S., O.E.S., C.F.F., and D.N.H. critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Figures


Comment on
-
How can registries and innovation improve surgical care?Lancet. 2016 Oct 1;388(10052):1349. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31763-9. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27707473 No abstract available.
-
Pakistan takes small steps towards tackling burn injuries.Lancet. 2016 Oct 1;388(10052):1366. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31770-6. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27707484 No abstract available.
References
-
- Herndon D, Tompkins R. Support of the metabolic response to burn injury. Lancet. 2004;363:1895–902. - PubMed
-
- Long C, Schaffel N, Geiger J, Schiller W, Blakemore W. Metabolic response to injury and illness: estimation of energy and protein needs from indirect calorimetry and nitrogen balance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1979;3:452–6. - PubMed
-
- Calvano SE, Xiao W, Richards DR, et al. A network-based analysis of systemic inflammation in humans. Nature. 2005;437:1032–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

