Intranasal administration of IL-35 inhibits allergic responses and symptoms in mice with allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 27707583
- PMCID: PMC7130026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.08.014
Intranasal administration of IL-35 inhibits allergic responses and symptoms in mice with allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: IL-35 was recently identified as an anti-inflammatory cytokine. We previously reported that recombinant fusion protein of murine IL-35 and human IgG1 Fc fragment (rIL-35) reduced Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-5) in vitro. However, it is unclear whether IL-35 can attenuate nasal allergic responses and symptoms of allergic rhinitis in vivo.
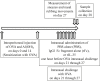
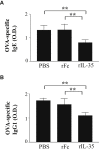
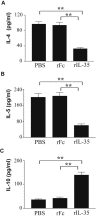
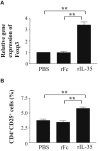
Methods: To investigate the in vivo effect of IL-35 on allergic rhinitis in mice, mice were sensitized with ovalbumin (OVA). Intranasal administration of rIL-35 and intranasal challenge of OVA were then performed. Nasal symptoms were estimated after the last nasal challenge. Nasal tissue and cervical lymph nodes (CLN) were collected. OVA-specific IgE in sera, OVA-specific T cell response, and the production of cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10) stimulated by the OVA antigen were measured. The transcription level of Foxp3 and the frequency of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells were also measured.
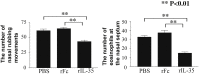
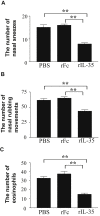
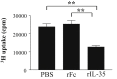
Results: rIL-35 significantly inhibited the number of sneezes and nasal rubbing movements. It also reduced the number of eosinophils in the nasal mucosa and significantly decreased the level of OVA-specific IgE, the OVA-specific T cell proliferation, and the production of IL-4 and IL-5. Furthermore, rIL-35 significantly increased the production of IL-10, the transcription level of Foxp3, and the frequency of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.
Conclusions: This study showed for the first time that rIL-35 inhibits nasal allergic responses and symptoms in mice, and that rIL-35 increases IL-10, Foxp3, and CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in CLN. This study also suggests that intranasal administration of IL-35 can attenuate allergic rhinitis.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Cervical lymph node; IL-10; IL-35; Regulatory T cell.
Copyright © 2016 Japanese Society of Allergology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranasal Administration of IL-27 Ameliorates Nasal Allergic Responses and Symptoms.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;178(2):101-105. doi: 10.1159/000493398. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30428479
-
Interleukin-37 Relieves Allergic Inflammation in a House Dust Mite Allergic Rhinitis Murine Model.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017 Oct;16(5):404-417. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29149780
-
Intralymphatic treatment of flagellin-ovalbumin mixture reduced allergic inflammation in murine model of allergic rhinitis.Allergy. 2016 May;71(5):629-39. doi: 10.1111/all.12839. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Allergy. 2016. PMID: 26752101
-
Interleukin-22 in Allergic Airway Diseases: A Systematic Review.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020 Mar;40(3):125-130. doi: 10.1089/jir.2019.0094. Epub 2019 Dec 31. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020. PMID: 31895598
-
T Cell-Mediated Nasal Hyperresponsiveness in Allergic Rhinitis.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43(1):36-40. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-01021. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 31902929 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T Cells in Allergy and Asthma.Front Pediatr. 2017 May 23;5:117. doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00117. eCollection 2017. Front Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28589115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurine promotes the production of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Treg cells through regulating IL-35/STAT1 pathway in a mouse allergic rhinitis model.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021 Jun 19;17(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13223-021-00562-1. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34147127 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal administration of regulatory dendritic cells is useful for the induction of nasal mucosal tolerance in a mice model of allergic rhinitis.World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Aug 11;13(8):100447. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100447. eCollection 2020 Aug. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32817781 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of IL-35 on the Expression of Nasal Epithelial-Derived Proinflammatory Cytokines.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Dec 3;2021:1110671. doi: 10.1155/2021/1110671. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34899052 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of mRNA profiles and identification of microRNA-mRNA network in CD4+ T cells in seasonal allergic rhinitis.J Int Med Res. 2022 Aug;50(8):3000605221113918. doi: 10.1177/03000605221113918. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35942560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aluvihare V.R., Kallikourdis M., Betz A.G. Regulatory T cells mediate maternal tolerance to the fetus. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:266–271. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M., Zheng X., Zhang X., Zhang Z.X., Ichim T.E., Sun H. A novel allergen-specific therapy for allergy using CD40-silenced dendritic cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M., Zheng X., Zhang X., Li M., Vladau C., Ichim T.E. Novel vaccination for allergy through gene silencing of CD40 using small interfering RNA. J Immunol. 2008;180:8461–8469. - PubMed
-
- Collison L.W., Workman C.J., Kuo T.T., Boyd K., Wang Y., Vignali K.M. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature. 2007;450:566–569. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

