Liver glucose metabolism in humans
- PMID: 27707936
- PMCID: PMC5293555
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160385
Liver glucose metabolism in humans
Abstract
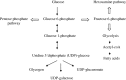
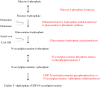
Information about normal hepatic glucose metabolism may help to understand pathogenic mechanisms underlying obesity and diabetes mellitus. In addition, liver glucose metabolism is involved in glycosylation reactions and connected with fatty acid metabolism. The liver receives dietary carbohydrates directly from the intestine via the portal vein. Glucokinase phosphorylates glucose to glucose 6-phosphate inside the hepatocyte, ensuring that an adequate flow of glucose enters the cell to be metabolized. Glucose 6-phosphate may proceed to several metabolic pathways. During the post-prandial period, most glucose 6-phosphate is used to synthesize glycogen via the formation of glucose 1-phosphate and UDP-glucose. Minor amounts of UDP-glucose are used to form UDP-glucuronate and UDP-galactose, which are donors of monosaccharide units used in glycosylation. A second pathway of glucose 6-phosphate metabolism is the formation of fructose 6-phosphate, which may either start the hexosamine pathway to produce UDP-N-acetylglucosamine or follow the glycolytic pathway to generate pyruvate and then acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA may enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucose 6-phosphate may produce NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate through the pentose phosphate pathway. Glucose metabolism supplies intermediates for glycosylation, a post-translational modification of proteins and lipids that modulates their activity. Congenital deficiency of phosphoglucomutase (PGM)-1 and PGM-3 is associated with impaired glycosylation. In addition to metabolize carbohydrates, the liver produces glucose to be used by other tissues, from glycogen breakdown or from de novo synthesis using primarily lactate and alanine (gluconeogenesis).
Keywords: diabetes; glucokinase; glucose; hexosamine pathway; pentose phosphate pathway.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures
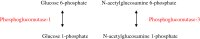
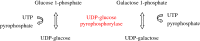
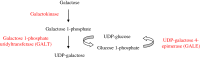
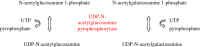

References
-
- Ferrannini E., Bjorkman O., Reichard G.A., Jr, Pilo A., Olsson M., Wahren J., DeFronzo R.A. The disposal of an oral glucose load in healthy subjects. A quantitative study. Diabetes. 1985;34:580–588. - PubMed
-
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R.L., Fukushima Y., Byers M.G., Shows T.B., Bell G.I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1988;85:5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

