Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3
- PMID: 27708076
- PMCID: PMC5510615
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aah3374
Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3
Abstract
Emerging evidence indicates that the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) may be due to cell-to-cell transmission of misfolded preformed fibrils (PFF) of α-synuclein (α-syn). The mechanism by which α-syn PFF spreads from neuron to neuron is not known. Here, we show that LAG3 (lymphocyte-activation gene 3) binds α-syn PFF with high affinity (dissociation constant = 77 nanomolar), whereas the α-syn monomer exhibited minimal binding. α-Syn-biotin PFF binding to LAG3 initiated α-syn PFF endocytosis, transmission, and toxicity. Lack of LAG3 substantially delayed α-syn PFF-induced loss of dopamine neurons, as well as biochemical and behavioral deficits in vivo. The identification of LAG3 as a receptor that binds α-syn PFF provides a target for developing therapeutics designed to slow the progression of PD and related α-synucleinopathies.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
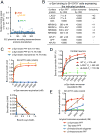
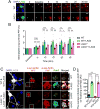
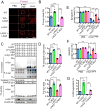
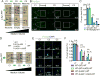

Comment in
-
Immune receptor for pathogenic α-synuclein.Science. 2016 Sep 30;353(6307):1498-1499. doi: 10.1126/science.aai9377. Science. 2016. PMID: 27708090 No abstract available.
References
-
- Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 2001;2:492–501. - PubMed
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Del Tredici K, Braak H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nature reviews. Neurology. 2013;9:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Mechanisms of Parkinson's disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron. 2006;52:33–38. - PubMed
-
- Dehay B, Vila M, Bezard E, Brundin P, Kordower JH. Alpha-synuclein propagation: New insights from animal models. Mov Disord. 2016;31:161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

