High-resolution interrogation of functional elements in the noncoding genome
- PMID: 27708104
- PMCID: PMC5144102
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf7613
High-resolution interrogation of functional elements in the noncoding genome
Abstract
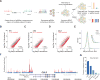
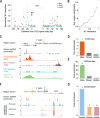
The noncoding genome affects gene regulation and disease, yet we lack tools for rapid identification and manipulation of noncoding elements. We developed a CRISPR screen using ~18,000 single guide RNAs targeting >700 kilobases surrounding the genes NF1, NF2, and CUL3, which are involved in BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. We find that noncoding locations that modulate drug resistance also harbor predictive hallmarks of noncoding function. With a subset of regions at the CUL3 locus, we demonstrate that engineered mutations alter transcription factor occupancy and long-range and local epigenetic environments, implicating these sites in gene regulation and chemotherapeutic resistance. Through our expansion of the potential of pooled CRISPR screens, we provide tools for genomic discovery and for elucidating biologically relevant mechanisms of gene regulation.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
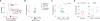
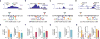
Comment in
-
Making the cut in the dark genome.Science. 2016 Nov 11;354(6313):705-706. doi: 10.1126/science.aak9849. Science. 2016. PMID: 27846591 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

