Effect of statins on disease-related outcomes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 27708114
- PMCID: PMC5284334
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208819
Effect of statins on disease-related outcomes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Data are conflicting regarding the possible effects of statins in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This post hoc analysis assessed the effects of statin therapy on disease-related outcomes in IPF.
Methods: Patients randomised to placebo (n=624) in three controlled trials of pirfenidone in IPF (CAPACITY 004 and 006, ASCEND) were categorised by baseline statin use. Outcomes assessed during the 1-year follow-up included disease progression, mortality, hospitalisation and composite outcomes of death or ≥10% absolute decline in FVC and death or ≥50 m decline in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD).
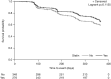
Results: At baseline, 276 (44%) patients were statin users versus 348 (56%) non-users. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups, except statin users were older and had higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease and risk factors. In multivariate analyses adjusting for differences in baseline characteristics, statin users had lower risks of death or 6MWD decline (HR 0.69; 95% CI 0.48 to 0.99, p=0.0465), all-cause hospitalisation (HR 0.58; 95% CI 0.35 to 0.94, p=0.0289), respiratory-related hospitalisation (HR 0.44; 95% CI 0.25 to 0.80, p=0.0063) and IPF-related mortality (HR 0.36; 95% CI 0.14 to 0.95, p=0.0393) versus non-users. Non-significant treatment effects favouring statin use were observed for disease progression (HR 0.75; 95% CI 0.52 to 1.07, p=0.1135), all-cause mortality (HR 0.54; 95% CI 0.24 to 1.21, p=0.1369) and death or FVC decline (HR 0.71; 95% CI 0.48 to 1.07, p=0.1032).
Conclusions: This post hoc analysis supports the hypothesis that statins may have a beneficial effect on clinical outcomes in IPF. Prospective clinical trials are required to validate these observations.
Trial registration numbers: NCT01366209, NCT00287729 and NCT00287716.
Keywords: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
MKr and his institution have received unrestricted grants and personal fees from InterMune International AG which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche in 2014, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and Boehringer Ingelheim. FB has received speaker fees, advisory board honoraria or grants from InterMune International AG which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche in 2014, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Serendex, Centocor and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. TMM is supported by a National Institute for Health Research Clinician Scientist Fellowship (NIHR Ref: CS:-2013-13-017). He has received research grants from GlaxoSmithKline, UCB and Novartis; and consulting and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biogen Idec, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Dosa, GlaxoSmithKline, Lanthio, InterMune International AG which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche in 2014, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Sanofi-Aventis, Takeda and UCB. UC has received grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Boehringer Ingelheim. He has received grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Intermune International AG which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche in 2014, and personal fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Bayer, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, UCB, Biogen and Centocor (all outside the submitted work). PS has received consulting fees from InterMune International AG which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche in 2014, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and Santhera Pharmaceuticals Ltd, and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis. DW is an employee of Policy Analysis Inc. (PAI), which received funding from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd for this study. K-UK is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Basel, Switzerland. MKo has served as site Principal Investigator in industry-sponsored clinical trials (Centocor, Roche, Sanofi and Boehringer Ingelheim) and is funded by the Canadian Institute for Health Research. He has served and/or serves on the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation Medical Advisory Board and on Advisory Boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche Canada, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Vertex, Genoa, Gilead, Janssen and Prometic.
Figures
Comment in
-
Time to share: lessons from post hoc analyses of IPF trials.Thorax. 2017 Feb;72(2):101-102. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209293. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Thorax. 2017. PMID: 27789650 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Durheim MT, Collard HR, Roberts RS, et al. . Association of hospital admission and forced vital capacity endpoints with survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: analysis of a pooled cohort from three clinical trials. Lancet Respir Med 2015;3:388–96. 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00093-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical