Superantigens hyperinduce inflammatory cytokines by enhancing the B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor interaction
- PMID: 27708164
- PMCID: PMC5081635
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1603321113
Superantigens hyperinduce inflammatory cytokines by enhancing the B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor interaction
Abstract
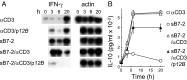
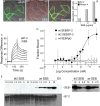
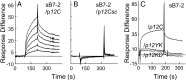
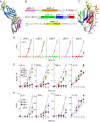
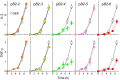
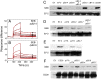
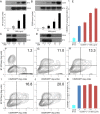
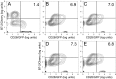
Full T-cell activation requires interaction between the costimulatory receptors B7-2 and CD28. By binding CD28, bacterial superantigens elicit harmful inflammatory cytokine overexpression through an unknown mechanism. We show that, by engaging not only CD28 but also its coligand B7-2 directly, superantigens potently enhance the avidity between B7-2 and CD28, inducing thereby T-cell hyperactivation. Using the same 12-aa β-strand-hinge-α-helix domain, superantigens engage both B7-2 and CD28 at their homodimer interfaces, areas remote from where these coreceptors interact, implying that inflammatory signaling can be controlled through the receptor homodimer interfaces. Short B7-2 dimer interface mimetic peptides bind diverse superantigens, prevent superantigen binding to cell-surface B7-2 or CD28, attenuate inflammatory cytokine overexpression, and protect mice from lethal superantigen challenge. Thus, superantigens induce a cytokine storm not only by mediating the interaction between MHC-II molecule and T-cell receptor but also, critically, by promoting B7-2/CD28 coreceptor engagement, forcing the principal costimulatory axis to signal excessively. Our results reveal a role for B7-2 as obligatory receptor for superantigens. B7-2 homodimer interface mimotopes prevent superantigen lethality by blocking the superantigen-host costimulatory receptor interaction.
Keywords: B7-2 dimer interface; costimulatory receptor; cytokine storm; superantigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal and Streptococcal Superantigens Trigger B7/CD28 Costimulatory Receptor Engagement to Hyperinduce Inflammatory Cytokines.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 30;10:942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00942. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31114583 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor engagement, a critical immune checkpoint.Receptors Clin Investig. 2017;4(1):e1500. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Receptors Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 28286804 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of superantigen toxins into the CD28 homodimer interface is essential for induction of cytokine genes that mediate lethal shock.PLoS Biol. 2011 Sep;9(9):e1001149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001149. Epub 2011 Sep 13. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21931534 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 6;10(11):459. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110459. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30404186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD28: direct and critical receptor for superantigen toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Sep 9;5(9):1531-42. doi: 10.3390/toxins5091531. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24022021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Administration of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Post-Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Exposure Protects Mice From Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 16;11:893. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00893. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32612530 Free PMC article.
-
Bystander Memory T Cells and IMiD/Checkpoint Therapy in Multiple Myeloma: A Dangerous Tango?Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;12:636375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636375. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal and Streptococcal Superantigens Trigger B7/CD28 Costimulatory Receptor Engagement to Hyperinduce Inflammatory Cytokines.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 30;10:942. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00942. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31114583 Free PMC article.
-
Superantigens, a Paradox of the Immune Response.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;14(11):800. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110800. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B (SEB) to B7 Receptors Triggers TCR- and CD28-Mediated Inflammatory Signals in the Absence of MHC Class II Molecules.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 13;12:723689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723689. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34489975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz JC, Zhang X, Fedorov AA, Nathenson SG, Almo SC. Structural basis for co-stimulation by the human CTLA-4/B7-2 complex. Nature. 2001;410(6828):604–608. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. The B7-CD28 superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(2):116–126. - PubMed
-
- Riley JL, June CH. The CD28 family: A T-cell rheostat for therapeutic control of T-cell activation. Blood. 2005;105(1):13–21. - PubMed
-
- Lindsten T, et al. Characterization of CTLA-4 structure and expression on human T cells. J Immunol. 1993;151(7):3489–3499. - PubMed
-
- Collins AV, et al. The interaction properties of costimulatory molecules revisited. Immunity. 2002;17(2):201–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

