The Important Role of Halogen Bond in Substrate Selectivity of Enzymatic Catalysis
- PMID: 27708371
- PMCID: PMC5052520
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34750
The Important Role of Halogen Bond in Substrate Selectivity of Enzymatic Catalysis
Abstract
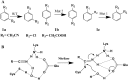
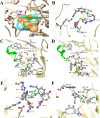
The use of halogen bond is widespread in drug discovery, design, and clinical trials, but is overlooked in drug biosynthesis. Here, the role of halogen bond in the nitrilase-catalyzed synthesis of ortho-, meta-, and para-chlorophenylacetic acid was investigated. Different distributions of halogen bond induced changes of substrate binding conformation and affected substrate selectivity. By engineering the halogen interaction, the substrate selectivity of the enzyme changed, with the implication that halogen bond plays an important role in biosynthesis and should be used as an efficient and reliable tool in enzymatic drug synthesis.
Figures
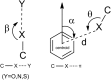
References
-
- Hernandes M. Z. et al.. Halogen atoms in the modern medicinal chemistry: hints for the drug design. Current drug targets 11, 303–314 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Lu Y. et al.. Halogen bonding for rational drug design and new drug discovery. Expert opinion on drug discovery 7, 375–383 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Xu Z. et al.. Halogen bond: its role beyond drug–target binding affinity for drug discovery and development. Journal of chemical information and modeling 54, 69–78 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Metrangolo P. & Resnati G. Halogen bonding: a paradigm in supramolecular chemistry. Chemistry-a European Journal 7, 2511–2519 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Hardegger L. A. et al.. Systematic investigation of halogen bonding in protein–ligand interactions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 50, 314–318 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

