The CSL proteins, versatile transcription factors and context dependent corepressors of the notch signaling pathway
- PMID: 27708688
- PMCID: PMC5037638
- DOI: 10.1186/s13008-016-0025-2
The CSL proteins, versatile transcription factors and context dependent corepressors of the notch signaling pathway
Abstract
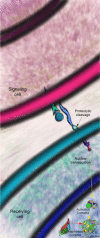
The Notch signaling pathway is a reiteratively used cell to cell communication pathway that triggers pleiotropic effects. The correct regulation of the pathway permits the efficient regulation of genes involved in cell fate decision throughout development. This activity relies notably on the CSL proteins, (an acronym for CBF-1/RBPJ-κ in Homo sapiens/Mus musculus respectively, Suppressor of Hairless in Drosophila melanogaster, Lag-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans) which is the unique transcription factor and DNA binding protein involved in this pathway. The CSL proteins have the capacity to recruit activation or repression complexes according to the cellular context. The aim of this review is to describe the different co-repressor proteins that interact directly with CSL proteins to form repression complexes thereby regulating the Notch signaling pathway in animal cells to give insights into the paralogous evolution of these co-repressors in higher eumetazoans and their subsequent effects at developmental processes.
Keywords: CSL; Embryo development; Hairless; Negative regulation; Notch signaling pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of murine RBPJ by Hairless protein matches that of Su(H) protein in the model system Drosophila melanogaster.Hereditas. 2021 Mar 28;158(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s41065-021-00175-z. Hereditas. 2021. PMID: 33775255 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancers with cooperative Notch binding sites are more resistant to regulation by the Hairless co-repressor.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 24;17(9):e1009039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009039. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34559800 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-independent functions of CSL.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;97:55-74. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385975-4.00009-7. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 22074602 Review.
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Drosophila Hairless/Su(H) heterodimer as a means of regulating Notch dependent transcription.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Oct;1866(10):1520-1532. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31326540
-
Keeping a good pathway down: transcriptional repression of Notch pathway target genes by CSL proteins.EMBO Rep. 2002 Sep;3(9):840-5. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf170. EMBO Rep. 2002. PMID: 12223465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of transducin-like enhancer of split (TLE) family proteins in tumorigenesis and immune regulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 11;10:1010639. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1010639. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36438567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between BEND5 and RBPJ suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis via inhibiting Notch signaling.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jun 27;18(10):4233-4244. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.70866. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35844785 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling determines cell-fate specification of the two main types of vomeronasal neurons of rodents.Development. 2022 Jul 1;149(13):dev200448. doi: 10.1242/dev.200448. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Development. 2022. PMID: 35781337 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of transcriptional repressors in the Notch signaling pathway: a computational analysis.Hereditas. 2019 Jan 17;156:5. doi: 10.1186/s41065-019-0081-0. eCollection 2019. Hereditas. 2019. PMID: 30679936 Free PMC article.
-
Taming the Notch Transcriptional Regulator for Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2018 Feb 15;23(2):431. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020431. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29462871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lai EC, Orgogozo V. A hidden program in Drosophila peripheral neurogenesis revealed: fundamental principles underlying sensory organ diversity. Dev Biol. 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bravo-Patino A, Baizabal-Aguirre VM. La vía de señalización Notch y el desarrollo embionario animal. REB. 2005;24(3–4):87–96.
-
- Mumm JS, Kopan R. Notch signaling: from the outside in. Dev Biol. 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

