Associations and Trends in Cause-Specific Rates of Death Among Persons Reported with HIV Infection, 23 U.S. Jurisdictions, Through 2011
- PMID: 27708746
- PMCID: PMC5037936
- DOI: 10.2174/1874613601610010144
Associations and Trends in Cause-Specific Rates of Death Among Persons Reported with HIV Infection, 23 U.S. Jurisdictions, Through 2011
Abstract
Background: Published death rates for persons with HIV have not distinguished deaths due to HIV from deaths due to other causes. Cause-specific death rates would allow better assessment of care needs.
Methods: Using data reported to the US national HIV surveillance system, we examined a) associations between selected decedent characteristics and causes of death during 2007-2011, b) trends in rates of death due to underlying causes among persons with AIDS during 1990-2011, and among all persons with diagnosed HIV infection (with or without AIDS) during 2000-2011.
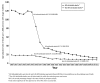
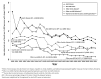
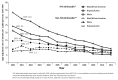
Results: During 2007-2011, non-HIV-attributable causes of death with the highest rates per 1,000 person-years were heart disease (2.0), non-AIDS cancers other than lung cancer (1.4), and accidents (0.8). During 1990-2011, among persons with AIDS, the annual rate of death due to HIV-attributable causes decreased by 89% (from 122.0 to 13.2), and the rate due to non-HIV-attributable-causes decreased by 57% (from 20.0 to 8.6), while the percentage of deaths caused by non-HIV-attributable causes increased from 11% to 43%. During 2000-2011, among persons with HIV infection, the rate of death due to HIV-attributable causes decreased by 69% (from 26.4 to 8.3), and the rate due to non-HIV-attributable causes decreased by 28% (from 10.5 to 7.6), while the percentage of deaths caused by non-HIV-attributable causes increased from 25% to 48%.
Conclusion: Among HIV-infected persons, as rates of death due to HIV-attributable causes decreased, rates due to non-HIV-attributable causes also decreased, but the percentages of deaths due to non-HIV-attributable causes, such as heart disease and non-AIDS cancers increased.
Keywords: AIDS; Associations; HIV-attributable causes of death; Non- HIV-attributable causes of death; Rate ratio; Trends; US national HIV surveillance system.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Revised surveillance case definition for HIV infection-United States, 2014. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2014;63(RR-03):1–10. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6303a1.htm?s_cid=rr6303a1_w . - PubMed
-
- Detels R., Tarwater P., Phair J.P., Margolick J., Riddler S.A., Muñoz A., Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Effectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapies on the incidence of opportunistic infections before and after AIDS diagnosis. AIDS. 2001;15(3):347–355. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200102160-00008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Detels R., Muñoz A., McFarlane G., Kingsley L.A., Margolick J.B., Giorgi J., Schrager L.K., Phair J.P., Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Investigators Effectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapy on time to AIDS and death in men with known HIV infection duration. JAMA. 1998;280(17):1497–1503. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.17.1497. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
