The Diagnosis and Management of Lipodystrophy Syndromes: A Multi-Society Practice Guideline
- PMID: 27710244
- PMCID: PMC5155679
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2016-2466
The Diagnosis and Management of Lipodystrophy Syndromes: A Multi-Society Practice Guideline
Abstract
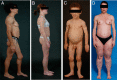
Objective: Lipodystrophy syndromes are extremely rare disorders of deficient body fat associated with potentially serious metabolic complications, including diabetes, hypertriglyceridemia, and steatohepatitis. Due to their rarity, most clinicians are not familiar with their diagnosis and management. This practice guideline summarizes the diagnosis and management of lipodystrophy syndromes not associated with HIV or injectable drugs.
Participants: Seventeen participants were nominated by worldwide endocrine societies or selected by the committee as content experts. Funding was via an unrestricted educational grant from Astra Zeneca to the Pediatric Endocrine Society. Meetings were not open to the general public.
Evidence: A literature review was conducted by the committee. Recommendations of the committee were graded using the system of the American Heart Association. Expert opinion was used when published data were unavailable or scarce.
Consensus process: The guideline was drafted by committee members and reviewed, revised, and approved by the entire committee during group meetings. Contributing societies reviewed the document and provided approval.
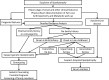
Conclusions: Lipodystrophy syndromes are heterogeneous and are diagnosed by clinical phenotype, supplemented by genetic testing in certain forms. Patients with most lipodystrophy syndromes should be screened for diabetes, dyslipidemia, and liver, kidney, and heart disease annually. Diet is essential for the management of metabolic complications of lipodystrophy. Metreleptin therapy is effective for metabolic complications in hypoleptinemic patients with generalized lipodystrophy and selected patients with partial lipodystrophy. Other treatments not specific for lipodystrophy may be helpful as well (eg, metformin for diabetes, and statins or fibrates for hyperlipidemia). Oral estrogens are contraindicated.
Figures
References
-
- Brown RJ, Gorden P. Leptin therapy in patients with lipodystrophy and syndromic insulin resistance. In: Dagogo-Jack S, ed. Leptin: Regulation and Clinical Applications. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2015:225–236.
-
- PG, Semb BK, Trygstad O, Seip M. Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac function and morphology in patients with generalised lipodystrophy. Eur J Pediatr. 1985;144(4):355–359. - PubMed
-
- Misra A, Garg A. Clinical features and metabolic derangements in acquired generalized lipodystrophy: case reports and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003;82(2):129–146. - PubMed
-
- Jackson SN, Howlett TA, McNally PG, O'Rahilly S, Trembath RC. Dunnigan-Kobberling syndrome: an autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy. QJM. 1997;90(1):27–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

