Signaling of Prostaglandin E Receptors, EP3 and EP4 Facilitates Wound Healing and Lymphangiogenesis with Enhanced Recruitment of M2 Macrophages in Mice
- PMID: 27711210
- PMCID: PMC5053515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162532
Signaling of Prostaglandin E Receptors, EP3 and EP4 Facilitates Wound Healing and Lymphangiogenesis with Enhanced Recruitment of M2 Macrophages in Mice
Abstract
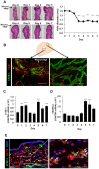
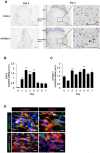
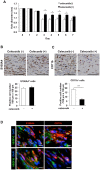
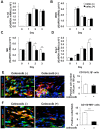
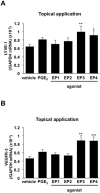
Lymphangiogenesis plays an important role in homeostasis, metabolism, and immunity, and also occurs during wound-healing. Here, we examined the roles of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) receptor (EP) signaling in enhancement of lymphangiogenesis in wound healing processes. The hole-punch was made in the ears of male C57BL/6 mice using a metal ear punch. Healing process and lymphangiogenesis together with macrophage recruitment were analyzed in EP knockout mice. Lymphangiogenesis was up-regulated in the granulation tissues at the margins of punched-hole wounds in mouse ears, and this increase was accompanied by increased expression levels of COX-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1. Administration of celecoxib, a COX-2 inhibitor, suppressed lymphangiogenesis in the granulation tissues and reduced the induction of the pro-lymphangiogenic factors, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) -C and VEGF-D. Topical applications of selective EP receptor agonists enhanced the expressions of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 and VEGF receptor-3. The wound-healing processes and recruitment of CD11b-positive macrophages, which produced VEGF-C and VEGF-D, were suppressed under COX-2 inhibition. Mice lacking either EP3 or EP4 exhibited reduced wound-healing, lymphangiogenesis and recruitment of M2 macrophages, compared with wild type mice. Proliferation of cultured human lymphatic endothelial cells was not detected under PGE2 stimulation. Lymphangiogenesis and recruitment of M2 macrophages that produced VEGF-C/D were suppressed in mice treated with a COX-2 inhibitor or lacking either EP3 or EP4 during wound healing. COX-2 and EP3/EP4 signaling may be novel targets to control lymphangiogenesis in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Roles of prostaglandin E2-EP3/EP4 receptor signaling in the enhancement of lymphangiogenesis during fibroblast growth factor-2-induced granulation formation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 May;31(5):1049-58. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.222356. Epub 2011 Feb 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21311040
-
Host prostaglandin EP3 receptor signaling relevant to tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2010 Feb;64(2):101-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2009.04.039. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20034758
-
Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 as the common target on cancer cells and macrophages to abolish angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, metastasis, and stem-like cell functions.Cancer Sci. 2014 Sep;105(9):1142-51. doi: 10.1111/cas.12475. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24981602 Free PMC article.
-
EP4 as a Therapeutic Target for Aggressive Human Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 29;19(4):1019. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041019. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29596308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of prostaglandins in tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis with special reference to breast cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018 Sep;37(2-3):369-384. doi: 10.1007/s10555-018-9734-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018. PMID: 29858743 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 (EP4) as a Therapeutic Target to Impede Breast Cancer-Associated Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;13(5):942. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050942. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of TP signaling promotes endometriosis growth and neovascularization.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Oct;28(4):192. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13079. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37654213 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the role of the mPGES-PGE₂-EP4 pathway in Escherichia coli-induced mastitis in dairy cows: insights for non-antibiotic therapeutic strategies.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 1;12:1628028. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1628028. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40666730 Free PMC article.
-
Intersecting Mechanisms of Hypoxia and Prostaglandin E2-Mediated Inflammation in the Comparative Biology of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 21;11:539361. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.539361. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAMP1 signaling in immune cells regulates inflammation-associated lymphangiogenesis.Lab Invest. 2020 May;100(5):738-750. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0364-0. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Lab Invest. 2020. PMID: 31911634
References
-
- Kurashige C, Hosono K, Matsuda H, Tsujikawa K, Okamoto H, Majima M. Roles of receptor activity-modifying protein 1 in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis during skin wound healing in mice. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2014;28(3):1237–47. Epub 2013/12/07. 10.1096/fj.13-238998 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

