Bmp4-Msx1 signaling and Osr2 control tooth organogenesis through antagonistic regulation of secreted Wnt antagonists
- PMID: 27713059
- PMCID: PMC5416936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.10.001
Bmp4-Msx1 signaling and Osr2 control tooth organogenesis through antagonistic regulation of secreted Wnt antagonists
Abstract
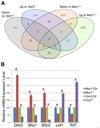
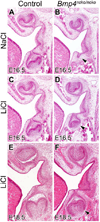
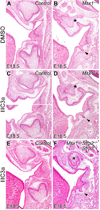
Mutations in MSX1 cause craniofacial developmental defects, including tooth agenesis, in humans and mice. Previous studies suggest that Msx1 activates Bmp4 expression in the developing tooth mesenchyme to drive early tooth organogenesis. Whereas Msx1-/- mice exhibit developmental arrest of all tooth germs at the bud stage, mice with neural crest-specific inactivation of Bmp4 (Bmp4ncko/ncko), which lack Bmp4 expression in the developing tooth mesenchyme, showed developmental arrest of only mandibular molars. We recently demonstrated that deletion of Osr2, which encodes a zinc finger transcription factor expressed in a lingual-to-buccal gradient in the developing tooth bud mesenchyme, rescued molar tooth morphogenesis in both Msx1-/- and Bmp4ncko/ncko mice. In this study, through RNA-seq analyses of the developing tooth mesenchyme in mutant and wildtype embryos, we found that Msx1 and Osr2 have opposite effects on expression of several secreted Wnt antagonists in the tooth bud mesenchyme. Remarkably, both Dkk2 and Sfrp2 exhibit Osr2-dependent preferential expression on the lingual side of the tooth bud mesenchyme and expression of both genes was up-regulated and expanded into the tooth bud mesenchyme in Msx1-/- and Bmp4ncko/ncko mutant embryos. We show that pharmacological activation of canonical Wnt signaling by either lithium chloride (LiCl) treatment or by inhibition of DKKs in utero was sufficient to rescue mandibular molar tooth morphogenesis in Bmp4ncko/ncko mice. Furthermore, whereas inhibition of DKKs or inactivation of Sfrp2 alone was insufficient to rescue tooth morphogenesis in Msx1-/- mice, pharmacological inhibition of DKKs in combination with genetic inactivation of Sfrp2 and Sfrp3 rescued maxillary molar morphogenesis in Msx1-/- mice. Together, these data reveal a novel mechanism that the Bmp4-Msx1 pathway and Osr2 control tooth organogenesis through antagonistic regulation of expression of secreted Wnt antagonists.
Keywords: Bmp4; Dkk2; Mouse; Msx1; Organogenesis; Osr2; Sfrp2; Tooth development; Wnt signaling.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE. WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev. Cell. 2002;2:643–653. - PubMed
-
- Bei M, Kratochwil K, Maas RL. BMP4 rescues a non-cell-autonomous function of Msx1 in tooth development. Development. 2000;127:4711–4718. - PubMed
-
- Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, Bringas P, Jr, Han J, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP, Sucov HM. Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development. 2000;127:1671–1679. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

